Developed by MolSoft in Collaboration with Medicinal Chemists at Novartis.
Introduction
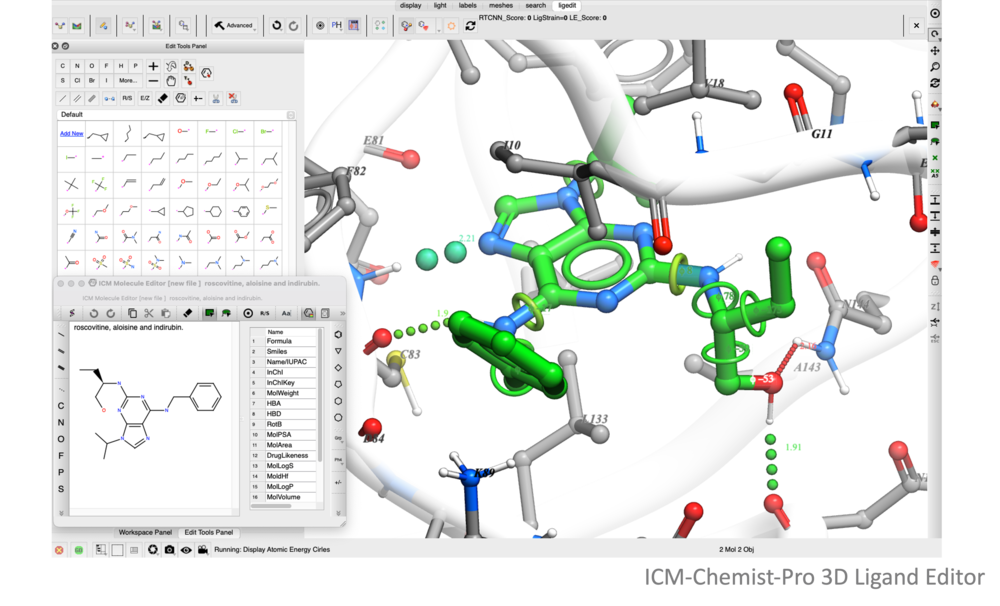
The ICM Ligand Editor is an intuitive graphical interface for ligand optimization and drug design. The editor was developed in close collaboration with Medicinal Chemists at Novartis and designed for ease of use and high accuracy ligand modeling. The ligand editor is available in ICM-Pro and ICM-Chemist-Pro.
A ligand can be modified in 2D or 3D and the effects of the modification can be seen on the binding energy to the receptor. For example a substituent can be changed with a single click on the screen and a calculation of the ligand binding score is made on the fly. The changes are stored and full undo and redo options are available and if the chemist likes the change they can tag and save the ligand in a chemical spreadsheet. Predictions are powered by MolSoft's high accurate docking ICM docking software. A wide set of tools are available for constrained docking using tethers and distance restraints as well as fragment and covalent docking. There are options for explicit flexible side-chains and multiple receptor docking to account for induced fit. The ligand editor can also be used for 3D pharmacophore ligand design using Atomic Property Fields.
Key Features
Ligand Editing
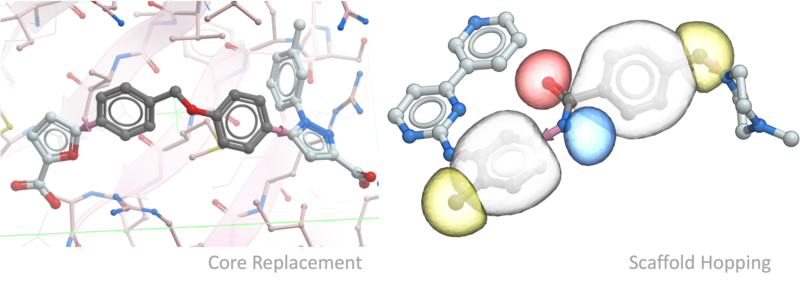
Ligand editing is a key step in structure-based drug design, enabling the optimization of molecular structures for better binding affinity, selectivity, and drug-like properties. Small modifications, such as fragment replacements or scaffold changes, can have a significant impact on activity. Precise editing tools allow researchers to explore structure-activity relationships and refine hits into viable leads.
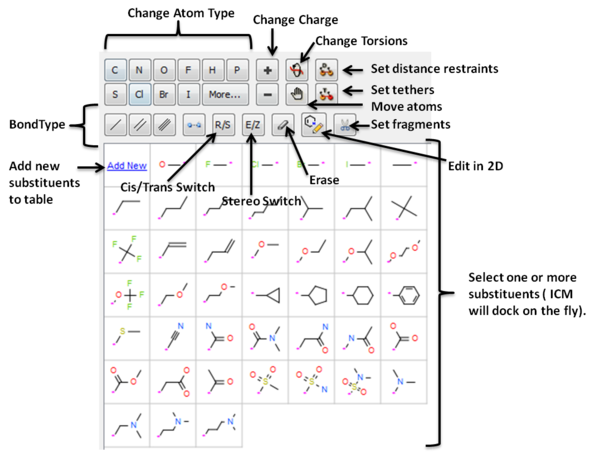
- Interactively edit a ligand bound to a receptor in 2D or 3D and see the effect on ligand binding.
- Change atom and bond types with a single click
- Switch stereo, cis and trans.
- Delete atoms and bonds.
- Rotate torsion angles.
- Sample one or more substituents at defined points around the ligand.
- Screen a database of substituents to a specific atom of a ligand - Fast virtual docking and scoring of replacement groups.
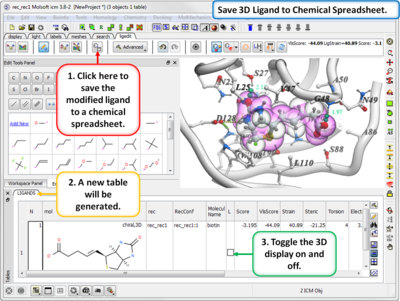
- Modification history table: Every ligand modification is stored and recorded in a chemical spreadsheet. Double click on the spreadsheet to view the change.
- Hetero atom scan around ligand: This option allows you to scan groups and hetero atoms at multiple locations on the ligand.
- R-group scan around ligand: This option allows you to scan groups and hetero atoms at multiple locations on the ligand.
- Fast core replacement and linker screening.
- Convenient undo and redo modification feature.
- Save new ligands in chemical spreadsheet export to Excel, SDF, Mol or PDB format.
- Modification history table: Every ligand modification is stored and recorded in a chemical spreadsheet. Double-click on the spreadsheet to view the change.
Docking and Minimization
Docking and minimization help refine ligand interactions within the binding site, making them essential tools in the 3D ligand editor. Docking provides an initial pose prediction, while minimization optimizes the ligand's conformation by resolving clashes and improving complementarity with the protein. These steps enhance the accuracy of ligand modifications, ensuring structural changes lead to meaningful improvements in binding.
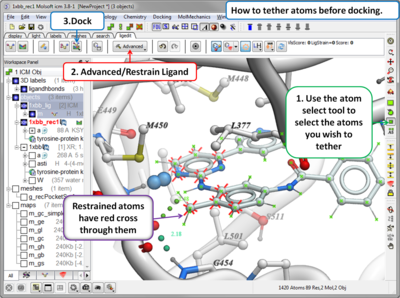
- Dock or Minimize a ligand inside a ligand binding pocket
- Calculate docking score and strain
- Dock using tethers and distance restraints
- Dock allowing specific residues in the receptor to be flexible
- Display hydrogen bonds, binding pocket, unsatisfied hydrogen bonds, and atomic energy circles
- On the fly docking and scoring of replacement groups
- Fragment docking
- 4D docking for induced fit
- Covalent docking.
- Ligand-based dockign to APF 3D pharmacophore
Receptor-Ligand Interactions
Understanding receptor-ligand interactions is crucial for effective ligand modification in the 3D ligand editor. Visualizing key contacts, such as hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and steric clashes, helps guide structural refinements to enhance binding affinity and specificity. Identifying these interactions allows for more informed ligand edits, improving the chances of designing a potent and selective compound.
- Display hydrogen bonds
- Display receptor binding pocket surface
- Display ligand binding pocket surface
- Display unsatisfied hydrogen bonds
- Display atomic energy circles
- Display relaxed ligand
- One click 2D interaction diagram: This option creates a 2D interaction map between the ligand and receptor.
- Simple way to analyze ligand-receptor contacts.
![]()


 Ligand editing is a key step in structure-based drug design, enabling the optimization of molecular structures for better binding affinity, selectivity, and drug-like properties. Small modifications, such as fragment replacements or scaffold changes, can have a significant impact on activity. Precise editing tools allow researchers to explore structure-activity relationships and refine hits into viable leads.
Ligand editing is a key step in structure-based drug design, enabling the optimization of molecular structures for better binding affinity, selectivity, and drug-like properties. Small modifications, such as fragment replacements or scaffold changes, can have a significant impact on activity. Precise editing tools allow researchers to explore structure-activity relationships and refine hits into viable leads.

