Google Search: Keyword Search:
| Prev | ICM User's Guide 9.14 Effect of Mutation on Protein-Peptide | Next |
This option uses the same methodology as the effect of mutation on Protein-Protein interaction except that backbone in the peptide is flexible.
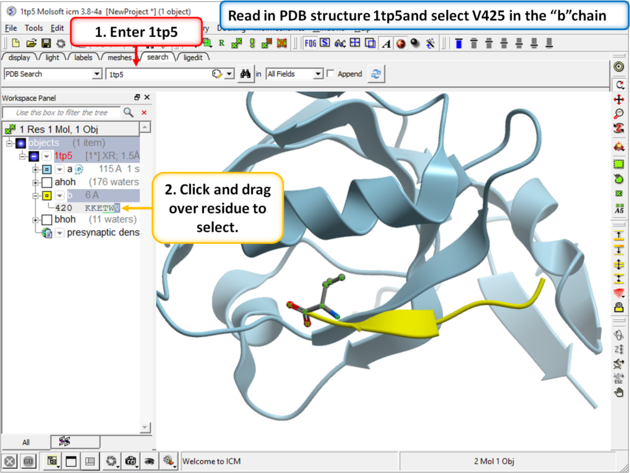 |
| Step 1 Read in your PDB structure. In this example we will use PDB 1 tp5 and select V425 in the peptide (b chain). |
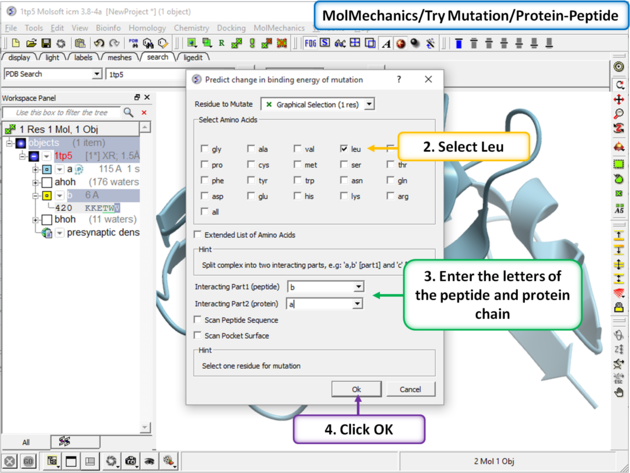 |
Step 2 In this example we will choose to see the effect of mutation of Val > Leu. Enter the letter of the chain for the interacting part 1 (peptide) and part 2 (protein). In addition you can choose:
|
 |
| Step 3 The simulation will run in the background and may take a while to finish if the option "all" or "Scan Sequence" is selected.
|
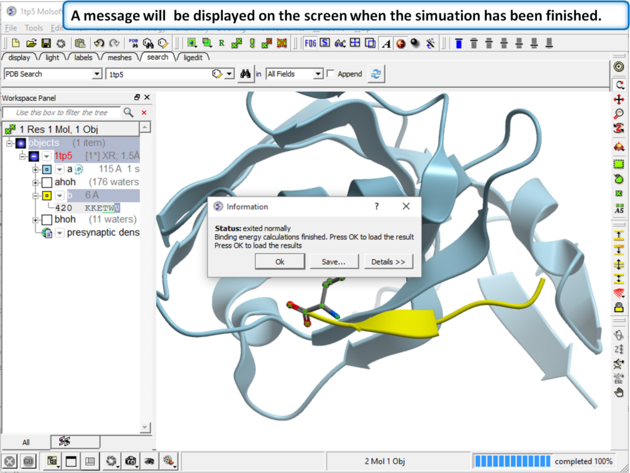 |
| Step 4 A message dialog box will let you know when your simulation has finished. |
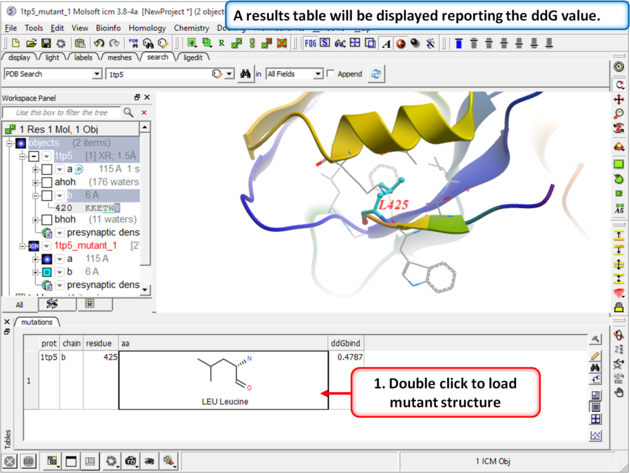 |
| Step 5 A table reporting the free energy change in peptide will be displayed (ddG kcal/mol). Double click a row of the table to load and display the mutated structure. |
How to interpret the results:
- ddG > 0: The mutation increases the free energy of folding, making the peptide binding less favorable.
- ddG < 0: The mutation decreases the free energy of folding, making the folded state more favorable.
- ddG ≈ 0: Suggests the mutation has little to no effect on peptide binding compared to wild type.
| Prev Mutation - Protein Stability | Home Up | Next Protein Ligand |