| Prev | ICM User's Guide 15.8 Chemical Search | Next |
[ Query | Filter Search | Processing | Text ]
Chemical similarity searching can be used to screen a database of compounds for structural similarity to a query chemical structure. The chemical similarity search window is shown below.
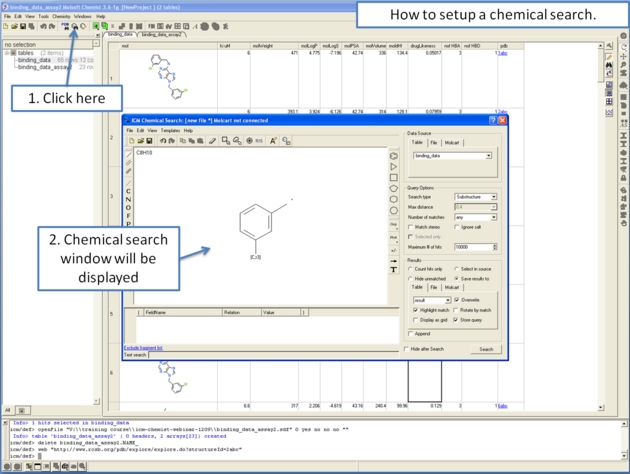
To access this window use the Tools/Chemical Search menu or select the button shown below.
15.8.1 Query Setup |
To set up a query first you must have either drawn or loaded a chemical structure into ICM. Instructions for this are described in the Reading Chemical Structures and Molecular Editor sections of this manual. If for example the query molecule you want to search is in a chemical spreadsheet you can right click on chemical in the spreadsheet and select Query Molecule.
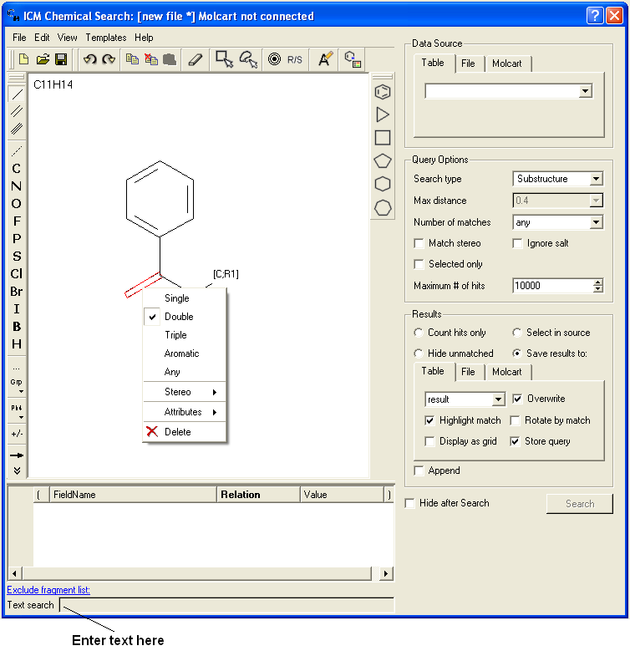
At this point your query can be modified as described in the Molecular Editor sections of this manual. However, there are a number of ways to specifically modify your query and filter your search. The way to accomplish this is to right click on a bond or atom and a menu as displayed below will be displayed. The menus differ depending on whether you right click on a bond or atom.
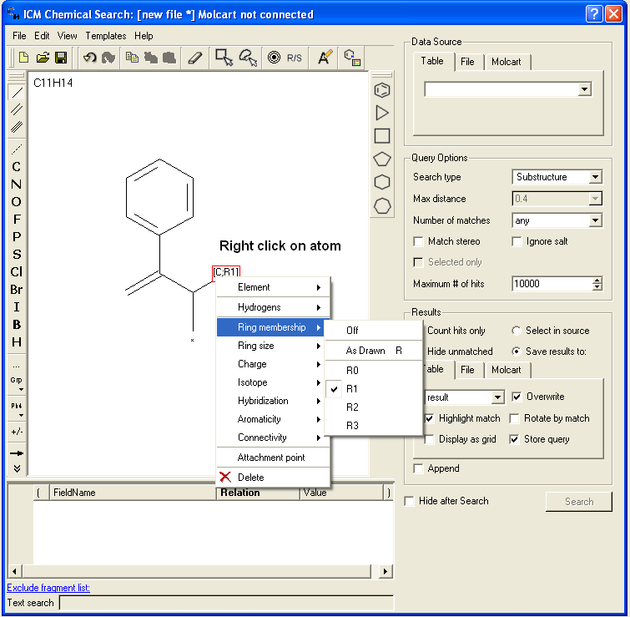
If you wish to specify a filter at an atom.
- Right click on the atom and the menu shown below will be displayed.
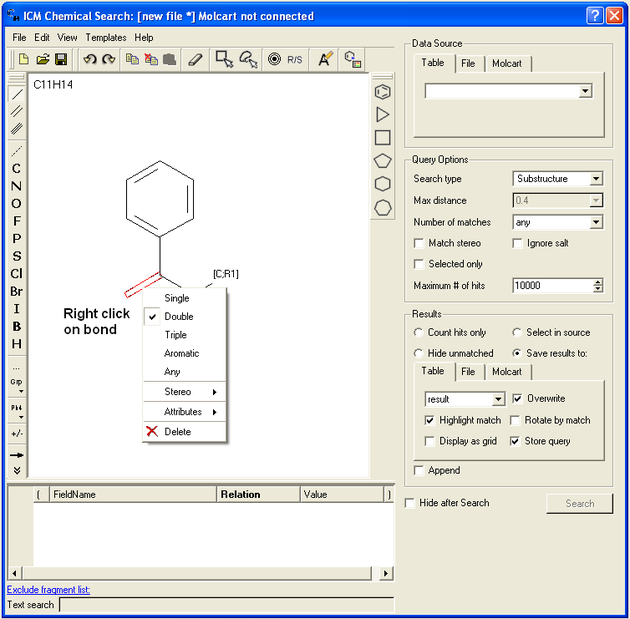
If you wish to specify a filter at a bond.
- Right click on the bond and the menu shown below will be displayed.
To specify a particular atom type, aromatic, aliphatic or R-group at a particular atom site.
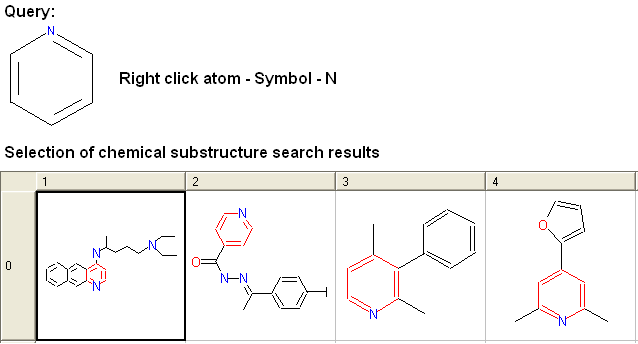
- Right click on the atom and select the "symbol" option as shown below.
- Select the desired atom type, aromatic, aliphatic or R-group and a symbol will be displayed as shown below.
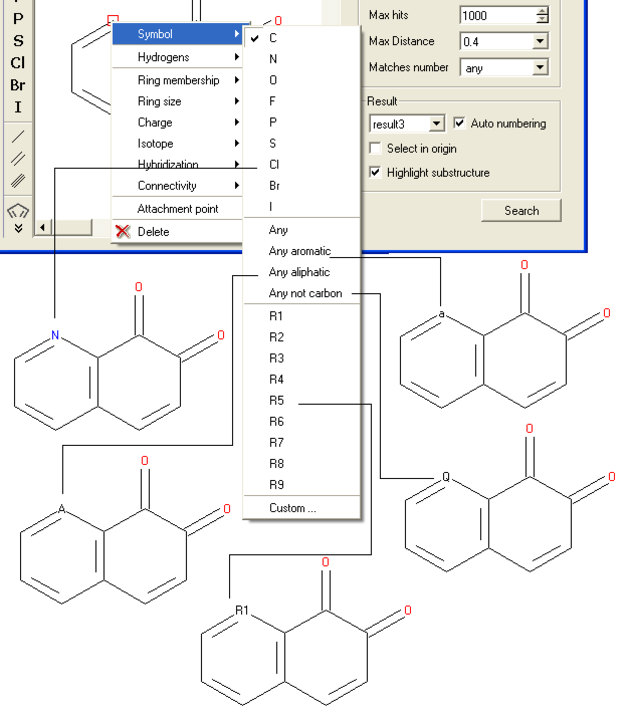
For example:
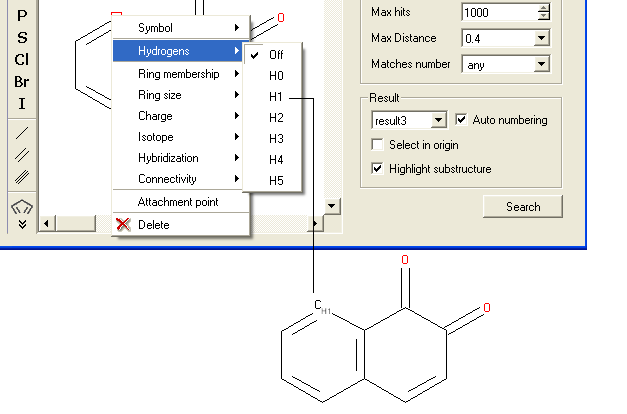
To specify a particular number of hydrogen atoms at a particular site:
- Right click on the atom and select the "Hydrogens" option as shown below.
- Select how many hydrogens you wish to specify and a symbol will be displayed as shown below.
To specify the number of rings a particular atom will be a member of:
- Right click on the atom and select the "Ring membership" option as shown below.
- Select whether the atom should be part of 1, 2 or 3 rings.
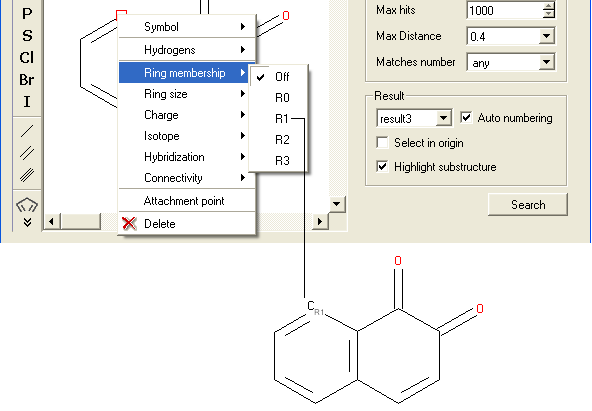
For example:
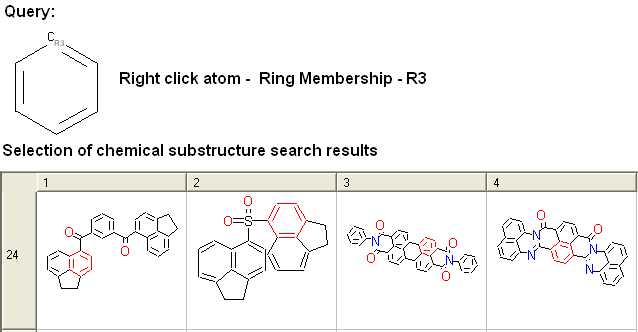
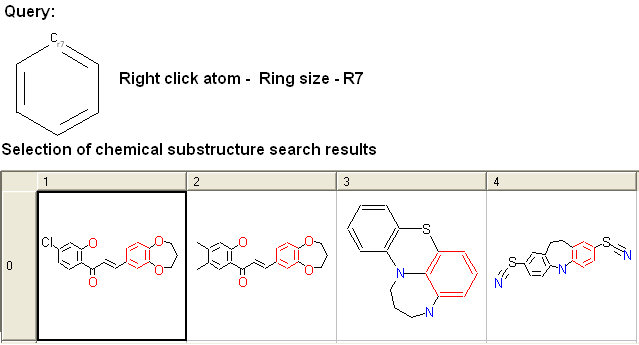
To specify the ring size connected to an atom:
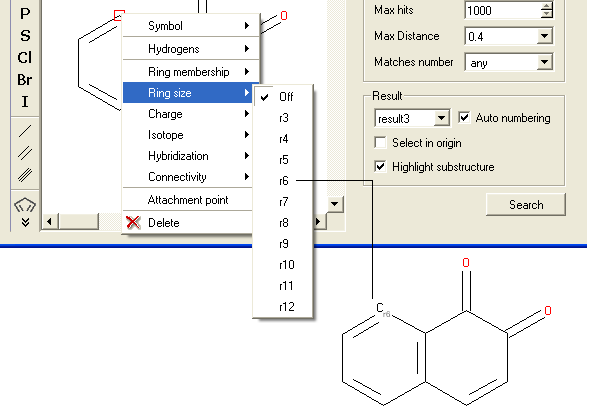
- Right click on the atom and select the "Ring size" option as shown below.
- Select the size of the ring the atom should be connected to and a symbol will be displayed as shown below.
For example:
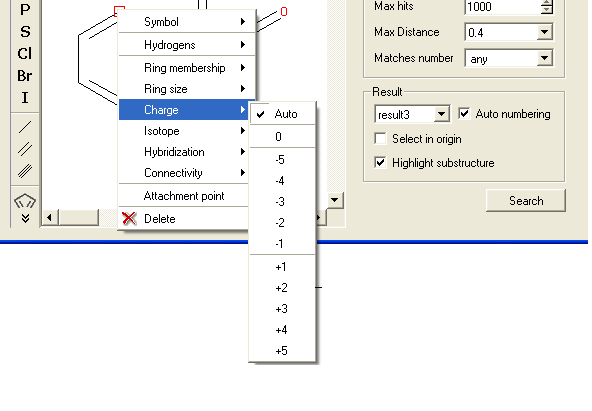
To specify the charge at a particular point:
- Right click on the atom and select the "Charge" option as shown below.
- Select the desired charge and a symbol will be displayed as shown below.
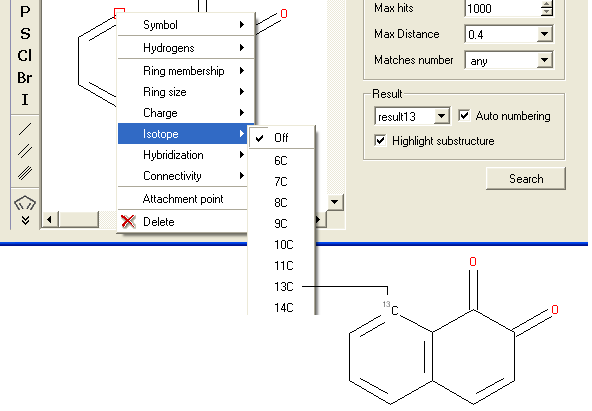
To specify an isotope at a particular atom
- Right click on the atom and select the "Isotope" option as shown below.
- Select the desired isotope from the list and a symbol as shown below will be displayed.
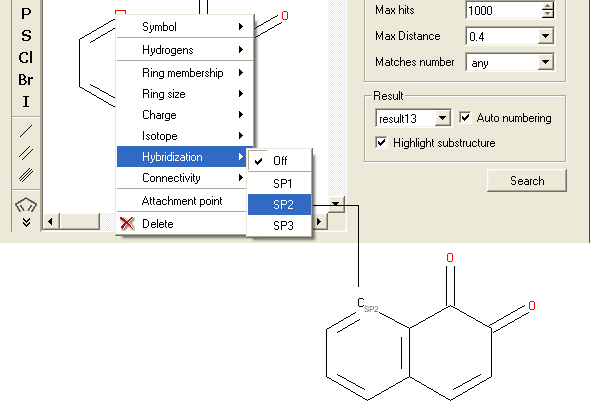
To specify the hybridization state of the atom:
- Right click on the atom and select the "Hybridization" option as shown below.
- Select the desired hybrization state and a symbol will be displayed as shown below.
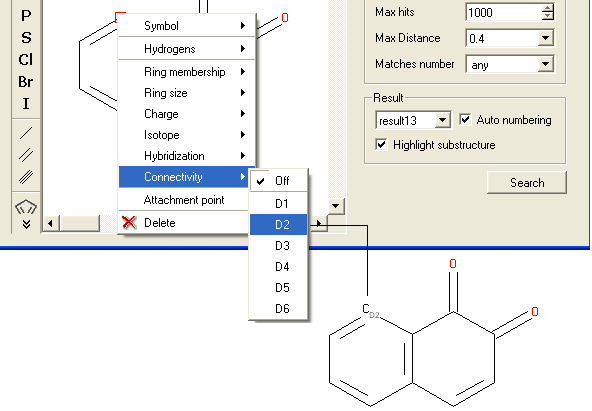
To specify the number of atoms you wish an atom to be connected to:
- Right click on the atom and select the "Connectivity" option as shown below.
- Select the number of atoms you wish the atom to be connected to and a symbol will be displayed as shown below.
To specify an attachment point - ie the position at which substituents will be added
- Right click on the atom and select the "Attachment point" option as shown below.
- An asterisk representing the attachment point will be displayed next to the atom.
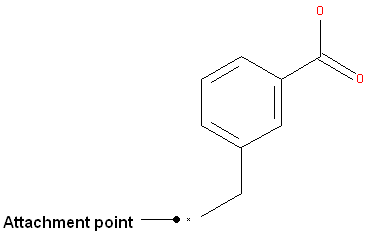
An attachment point means that the atom can be attached to zero or more bonds to heavy atoms.
15.8.2 Filter Search |
How to filter your query
To filter your query:
- Right click in the box shown below and select 'Add Condition'
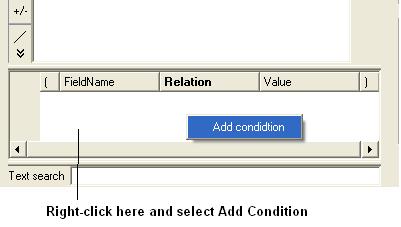
To add conditions to your filter:
- Double click in the fields labeled "Name" and "Relation" and select the options from the drop down arrow or type in values.
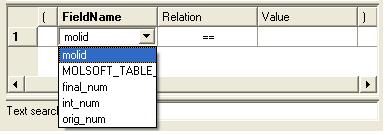
To remove a filter, right click on the filter and select 'Remove Filter'.
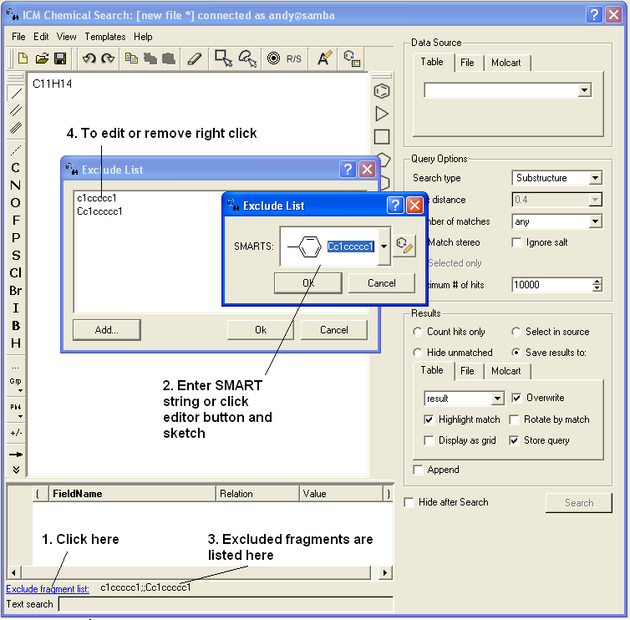
To exclude a fragment from your search
Click on the option Exclude fragment list:
- Enter the SMART string of the fragment or use the Molecular Editor option to sketch the fragment.
- Click OK and the fragment will be listed at the bottom of the chemical search window as shown below.
15.8.3 Query Processing |
To begin processing your query first you need to decide which database to search. The options are listed in the Data Source section of the ICM chemical search window.
Data Source
You can either search a Table- Chemical Spreadsheet a File - Local Database or MolCart.
If you select MolCart you first need to setup the link to the correct database.
- Enter the Server Name in which the database is stored.
- Enter the database name.
- Enter your username and password for the server.
- You can save these details so you dont have to re-enter this information each time you use the chemical similarity search.
If you are searching a Table, click on the Table tab and then select the drop down button where the names of your currently loaded tables are stored.
If you are searching a File click on the File tab and then locate your local database file .molt or if it is already loaded into ICM you can locate it with the drop down button.
Query Options
Now select a search type:
- Click on the drop down arrow next to the "Search Type" option in the Query Options panel.
- Select the search type you want to use.
A substructure search is a search whereby only the defined molecule in the query will be searched against the database. Whereas, a FP similarity search which stands for fingerprint search enables any fingerprint within a structure to be searched for in the database.
The Max distance option is available for use with the FP search and the Matches number option is for use with the substructure search. The option you do not require based on your search method will be blanked out. A "Max distance" value of 0 means that the search will only identify matches exactly the same as the fingerprint - the default is 0.4. The "Matches number" option allows you to stipulate how many times within a structure in the database your query can be found.
You can match stereo by selecting the Match stereo option and ignore salts. If you make a selection of your query ICM can use that selection to search. How to make selections in the Molecular Editor are described here. Enter the Maximum number(#) of hits you would like returned.
Results
Before processing the query determine how you would like your results displayed in the Results section of the Chemical Search window.
Count hits only - this option will count the number of hits and display this number in a window once the searching has been completed.
Select in source - If you are searching a table you can select and highlight the query in the source table that you are searching.
Hide unmatched - Hide unmatched will hide the compounds that were not matched from view.
Save results to: - this option gives you the option to save the output results to a Table- Chemical Spreadsheet a File -Local Database or MolCart.
Append - this option will allow you to append to current table, file or Molcart database.
Search
- Click on the Search button to execute the search. You can choose to hide the window after the search.
15.8.4 Search a Database by Text |
To search a database by text enter the text you wish to search in the Text Search data entry box at the bottom of the ICM Chemical Search window.
| Prev IUPAC | Home Up | Next Pharmacophore Search |