| Prev | ICM User's Guide 3.4 How to work with Protein Structures | Next |
[ Read PDB | Convert PDB | Convert | ICM Workspace | Graphical Display | Pocket Surface | Electrostatic Surface | Hydrogen Bond | Measure Distance ]
A quick start guide on how to display and analyse protein structure.
3.4.1 How to Read in a PDB File |
The easiest way to read a PDB file into ICM is to use the "pdb search" tab. You can use keyword searching or type in the PDB code you are interested in. An asterisk (*) wildcard can be used to list all the pdb files currently available in the protein databank. Different fields can be searched by using the drop down arrow as shown below.
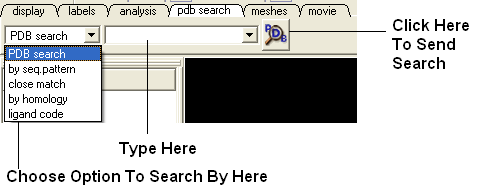
There are other PDB search options (such as search by sequence homology, identity , pattern ....) located at the bottom of the "Edit" menu.
Once a search is complete a table of PDB files relating to your search query will be displayed. To view the PDB file in 3D in the graphical display double click on a row in the PDBSearchResults table.
| NOTE: If you have a PDB structure already saved you can read it into ICM by going to the File Menu and selecting Open. |
3.4.2 How to Convert a Protein into an ICM Object |
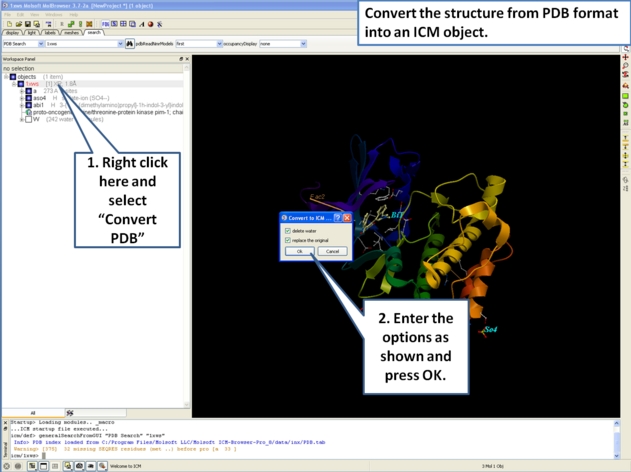
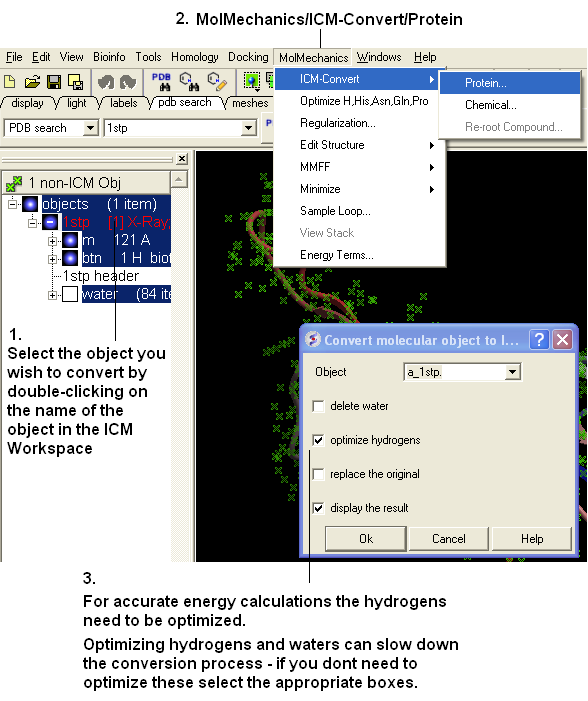
If you are going to make any energy calculation in ICM (eg docking, display H-bonds, display electrostatic and binding property surfaces etc..) it is necesary to convert a protein or chemical into an ICM object.
To convert a PDB structure into an ICM object follow the steps shown below:
In ICM-Browser-Pro:
OR
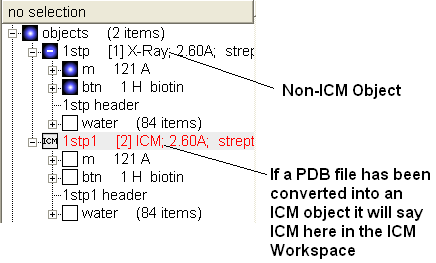
If your object is an ICM object it will tell you in the ICM Workspace:
3.4.3 How to Convert a Chemical from the PDB |
The protein data bank has not been storing any information about covalent bond types and formal charges of the chemical compounds interacting with proteins! This oversight makes it impossible to automatically convert those molecules to anything sensible and requires your manual interactive assignment of bond types and formal charges for each compound in a pdb-entry. Therefore, if you apply the convert command to a pdb-entry with ligands, the ligands will just become some crippled incomplete molecules that can not be further conformationally optimized.
Therefore, follow these steps to convert a chemical properly from a pdb form to a correct icm object. There are two ways to do this either via the ICM Workspace (recommended) or via the Graphical Display.
3.4.4 Converting a Chemical from the PDB using the ICM Workspace |
- File/Open PDB
- View the ligand in the ICM Workspace by expanding the molecule tree (see below).
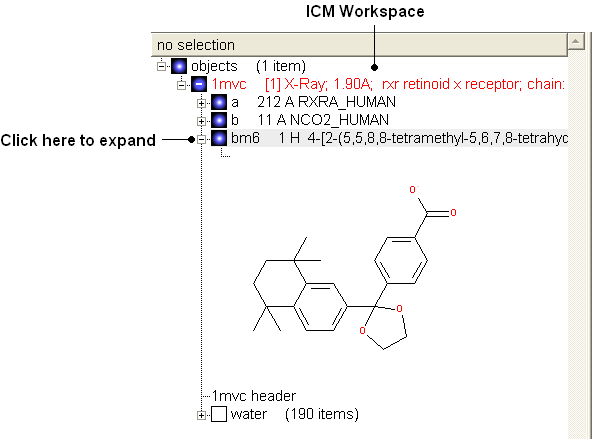
Change bond orders:
- Change the bond orders by selecting the bond (highlighted in red).
- Right click and select the desired bond as shown below.
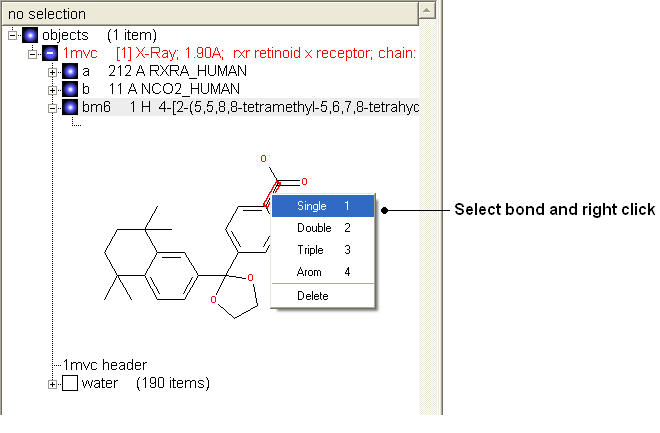
| NOTE: Keyboard shortcuts are provided to make editing faster. |
Change atom and charge:
- Change the atom or charge by selecting the atom (highlighted in red).
- Right ckick and select the desired atom or charge as shown below.
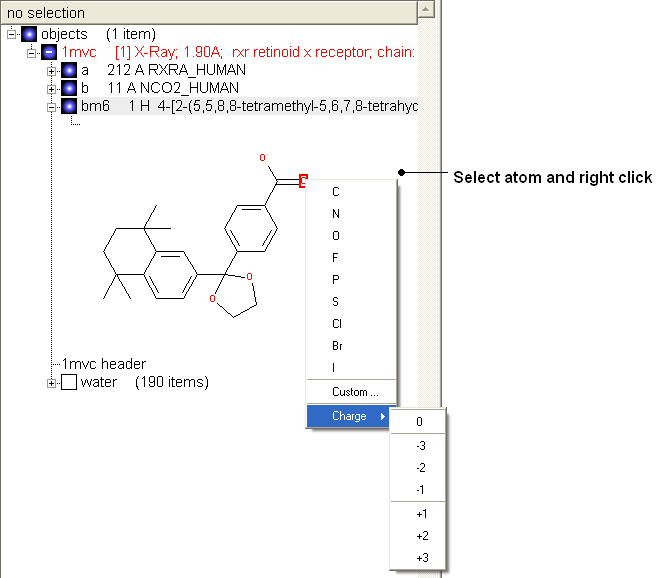
| NOTE: Keyboard shortcuts are provided to make editing faster. |
Convert to 3D in MMFF force field:
- Once you have made the changes to the ligand - right click on the name of the ligand in the ICM Workspace and select Move from Object.
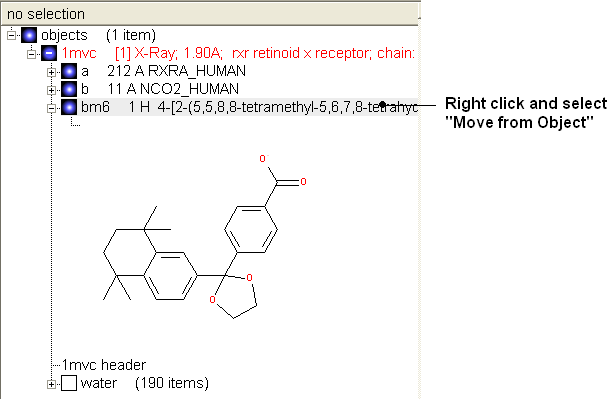
- Select the ligand by double clicking on it in the ICM Workspace.
- Select MolMechanics/ICM-Convert/Chemical
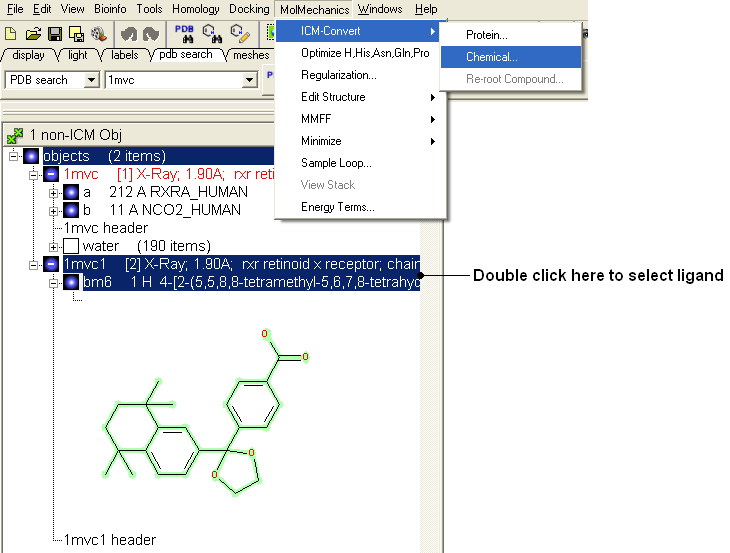
| NOTE: If you need to add an extra bond you will need to use the full molecular editor. Right click on the name of the ligand in the ICM Workspace and select Edit/Edit Compound. |
3.4.5 How to Convert a Chemical from the PDB using the Graphical Display |
- Display the molecule in wire chemistry style mode by right clicking on the Wire Representation button (see Wire Representation section).
To change the bond types in your ligand:
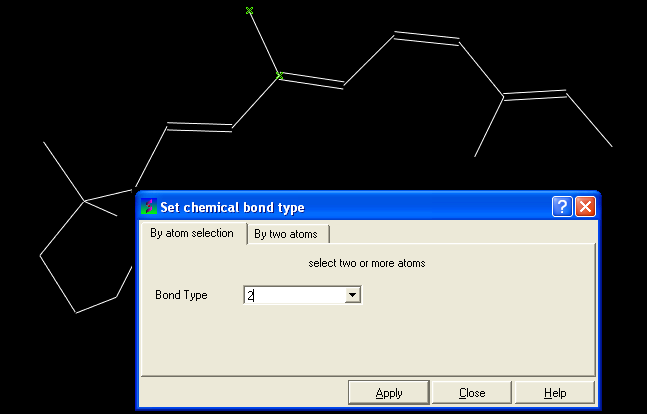
- Click on MolMechanics/Edit Structure/Set Bond Type and the Set chemical bond type data entry box will be displayed.
You can either select (see selection menu section)the atoms you wish to change graphically using the rectangular or lasoo selection button OR
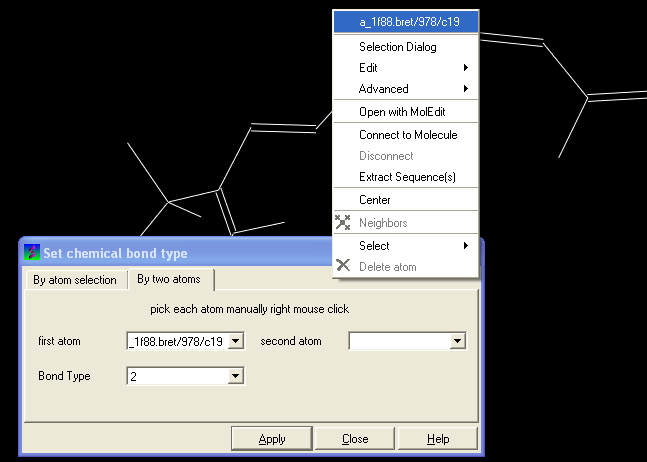
You can select the By two atoms tabs and right click on the atoms you wish to change and then selecting the atom descriptor with the left mouse button as shown below.
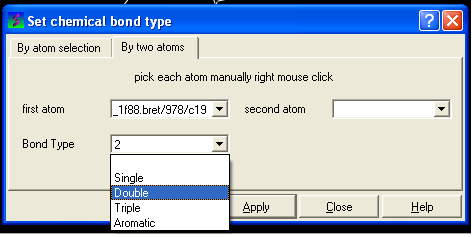
- Select the desired bond type either single, double, triple or aromatic.
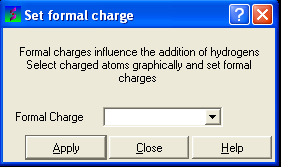
To set the formal charge of a compound:
Click on MolMechanics/Edit Structure/Set Formal Charge and then select the appropriate charge.
The final step is to convert the compound into an ICM object:
- Select the chemical (green crosses in graphical display).
- MolMechanics/ICM-Convert/Chemical
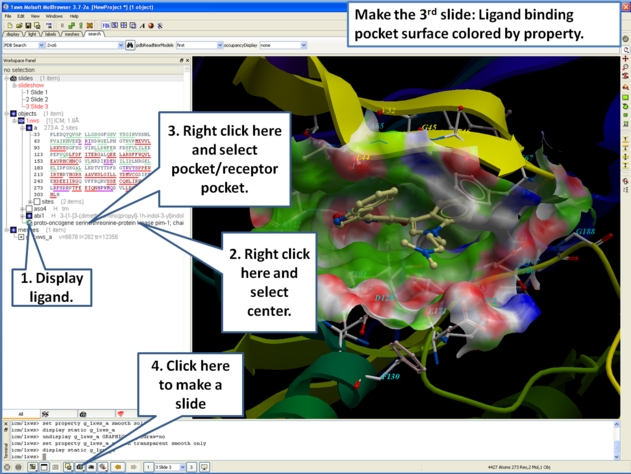
3.4.6 How to Display the Ligand Binding Pocket Surface and Neighboring Residues. |
- As an example we will use the PDB structure 1STP. Type 1STP in the pdb search tab and press return.
- Right click on the ligand "btn" and select "Ligand Pocket"
- To remove the ribbon display and display only the residues in the pocket. Select the "display" tab and click on the ribbon button which will undisplay the ribbon representation and leave only the residues surrounding the pocket.
3.4.7 How to Display Electrostatic Surfaces Around a Ligand. |
- As an example we will use the PDB structure 1STP. Type 1STP in the pdb search tab and press return.
- In order to display energy related properties we need to convert the PDB file into an ICM object. To convert 1STP into an ICM object follow the instructions Converting a Protein into an ICM Object. In this example, the option "Replace the Original" was selected.
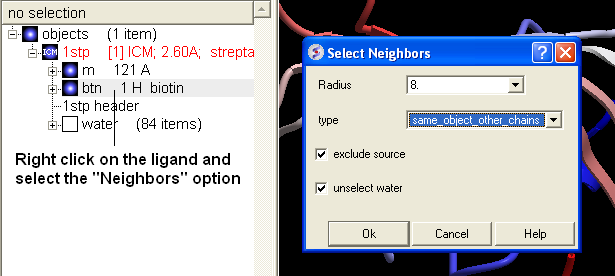
- Once the PDB file has been converted to an ICM object - right click on the ligand "btn" and select "Neighbors".
- Enter a Radius around which you wish to construct the surface. In the "Type" data entry box select "same_object_other_chains". A selection should be seen in the graphical display as green crosses.
- Select the meshes tab and use the drop-down arrow to select "electrostatics" as shown below.
- Click on the button (shown below) and the electrostatic surface of the binding pocket will be displayed.
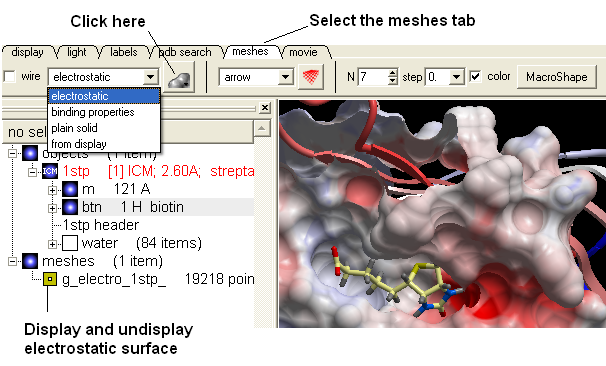
The surface can be displayed and undisplayed in the ICM Workspace by clicking in the box corresponding to the mesh. Negatively charged surface is colored red and positively charged is colored blue.
| NOTE: You can use the same process to color the pocket surface by binding property - just select "binding properties" from the drop down menu. Green is hydrophobic, red is hydrogen bond acceptor and blue is hydrogen bond donor. |
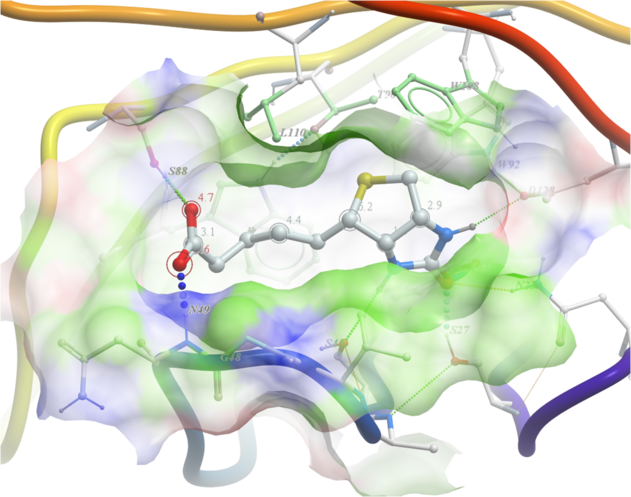
3.4.8 How to Display Hydrogen Bonds Between a Ligand and Receptor. |
| NOTE: The method by which hydrogen bonds are calculated is described here in the command line manual. The GRAPHICS.hbondMinStrength parameter determines the hbond strength threshold for hbond display. The strength value is between 0. and 2. By changing 1. to 0.2 you will see more weak hydrogen bonds. |
- As an example we will use the PDB structure 1STP. Type 1STP in the pdb search tab and press return.
- In order to display energy related properties we need to convert the PDB file into an ICM object. To convert 1STP into an ICM object follow the instructions Converting a Protein into an ICM Object. In this example, the option "Replace the Original" was selected.
- Display the receptor in wire format and the ligand in xstick.
- Right click on the ligand and select "Neighbors" - Enter 3 Angstroms and Type = Visible. Do not exclude source (the ligand) therefore remove tick from box entitled "exclude source".
- Select the display tab and then select the Display H-Bond button.
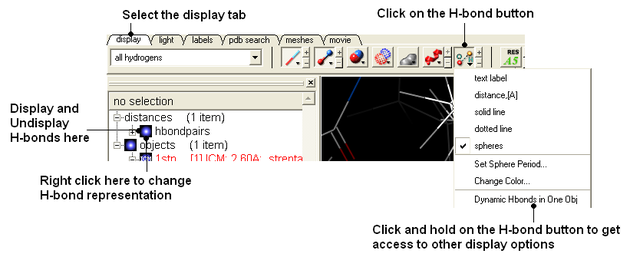
| NOTE: Different options for displaying the H-bond can be accessed by clicking and holding on the H-bond button in the "Display" tab. |
3.4.9 How to Measure the Distance Between Two Atoms. |
To calculate the distance between two atoms you must first select each atom. The easiest way to do this is to use the "Pick Atom" button.
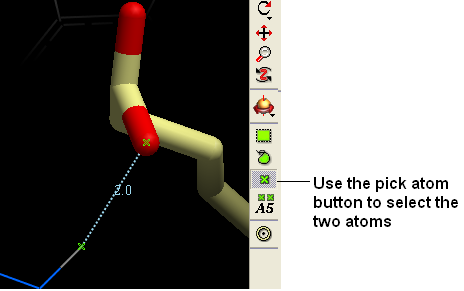
- Select the "Pick Atom" button"
- Click on the atoms you wish to select. A green cross should be displayed on the atom.
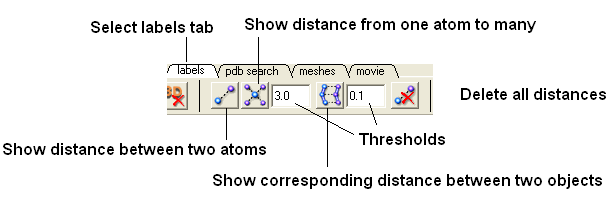
- Select the "Labels Tab" and select the distance button.
| Prev Drag & Drop | Home Up | Next Menu Option Guide |