Version: |
3.9-5 |
3.9-4 |
3.9-3 |
3.9-2 |
3.9-1 |
3.8-7 |
3.8-6 |
3.8-5 |
3.8-4 |
3.8 |
3.7
New features in our
products are summarized on this page. This is not a complete list and so please also see the
Release Notes.
You can download the latest version of ICM from our
Support Site or
contact us to use the Beta version.
Version 3.9-5
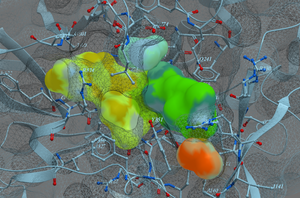
CombiRIDGE - High Throughput Combinatorial Anchored Docking for Virtual Screening of Vast Chemical Spaces
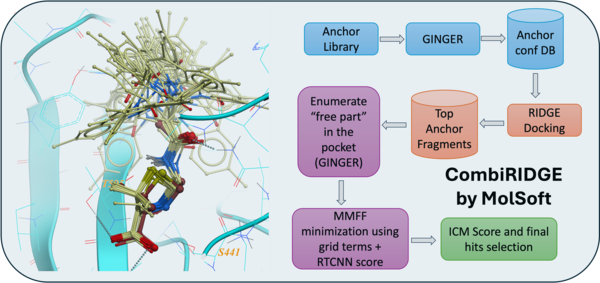
CombiRIDGE is a new innovative GPU-accelerated solution for high-throughput ligand docking and screening which leverages MolSoft's generative neural network conformer enumeration method GINGER, ultra-fast GPU docking technology RIDGE and advanced graph neural network scoring ( RTCNN ). The approach allows you to optimize specific R-groups and screen vast ultra-large or combinatorial libraries efficiently.
The anchor-driven approach begins with a 3D anchor or core fragment and a 2D R-group, anchoring the core within the binding site to maintain critical interactions. Using GINGER, full 3D conformers are generated directly at the binding site, allowing very rapid combinatorial expansion of pre-docked anchor structures into complete compounds that sample the full library space around each anchor fragment. Pose refinement is achieved through GPU-accelerated grid/MMFF energy minimization, optimizing poses for enhanced accuracy and consistency. Finally, advanced scoring using RTCNN evaluates docked poses, providing robust metrics for selecting high-quality candidates. Read More...
| Documentation | Webinar | Requires ICM-Pro + VLS + RIDGE + GINGER License
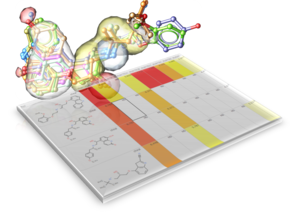
Announcing groupGen: Next-Generation Neural Network for Lead Optimization
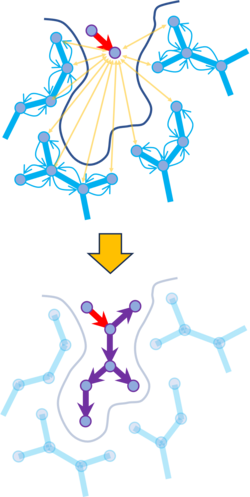
We are excited to introduce groupGen, a new generative AI technology designed specifically for lead optimization. groupGen focuses on generating high-quality R-group substitutions that are tailored to a defined protein binding site. By analyzing the local 3D receptor environment around a selected attachment point on a ligand, groupGen proposes chemically realistic substituents that are sterically compatible and optimized for binding.
At the core of groupGen is a context-aware neural network architecture that connects structural biology with chemical design. A 3D graph convolutional neural network examines the geometry, electrostatics, and hydrophobic features of the binding pocket to create a latent representation of the ideal substituent environment. This representation guides a chemical graph generator trained on millions of known R-groups, ensuring that suggested modifications are both target-relevant and chemically valid.
groupGen is tightly integrated into MolSoft’s structure-based discovery workflow. Generated analogs are automatically passed to CombiRidge for anchored docking, which preserves the core ligand pose while efficiently exploring substituent space. This enables rapid evaluation of many design ideas without disrupting the key interactions established by the original lead compound.
To prioritize the most promising candidates, groupGen applies a multi-stage ranking strategy. Docked compounds are first evaluated using RTCNN and VLS scores to assess binding quality, and are then filtered using a synthesizability score to favor structures that are practical to make. This combined approach delivers a focused set of high-confidence compounds that balance binding performance with synthetic feasibility, accelerating decision-making in lead optimization programs.
|
Documentation |
Ligand AIDE – de-novo ligand generation by Artificial Intelligent Design Evolution
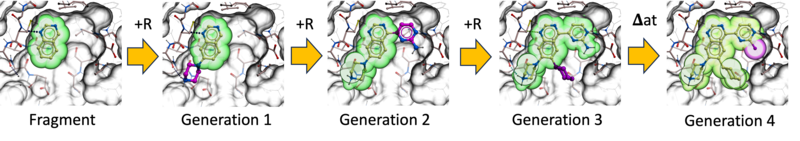
Ligand AIDE is a de novo ligand generation workflow based on Artificial Intelligent Design Evolution. It uses an iterative evolutionary strategy to grow and optimize ligands directly in the context of a protein binding site.
The process begins with a population of docked small fragments. From this starting point, new designs are generated by adding or replacing R-groups using the groupGen neural network, as well as by performing atom-level substitutions using the Atom Predictor. Each newly generated cohort of compounds is then re-docked into the binding site.
Designs are refined through multiple evolutionary cycles, typically three to five iterations. At each step, a Darwinian selection process removes poor designs based on several criteria, including RTCNN scores, physics-based binding scores with penalty terms, drug-like property filters, and synthesizability.
Through successive generations, fragments evolve into more complete and optimized ligands. This iterative grow-and-select strategy enables efficient exploration of chemical space while maintaining binding quality, drug-like behavior, and practical synthetic feasibility.
| Documentation | Requires ICM-Pro + VLS + AI License
New Comprehensive Peptide Modeling Workflows now available in MolSoft ICM-Pro 3D Interactive Ligand Editor
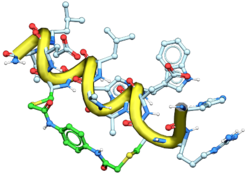
MolSoft ICM-Pro extends the Interactive Ligand Editor to support comprehensive peptide modeling workflows.
Peptides can be prepared, edited, and modeled with full continuous-chain handling and sequence-level control
directly within the ligand editor.
Residue-level operations include insertion, deletion, replacement, capping, and local optimization,
enabling rapid sequence and structural refinement.
Peptides can be modeled alone or in complex with the receptor.
Both peptide and receptor can be minimized and relaxed together.
Binding poses and conformational quality can be evaluated using RTCNN scoring and internal strain analysis.
Secondary structure refinement is supported through tools such as Reinforce Helix,
allowing stabilization and optimization of helical regions.
The ligand editor also supports modeling and exploration of stapled peptides,
enabling structure-based design and evaluation of conformationally constrained peptide ligands.
GigaSearch V2.0 - Efficient Massive Scale Similarity and Substructure Chemical Searching
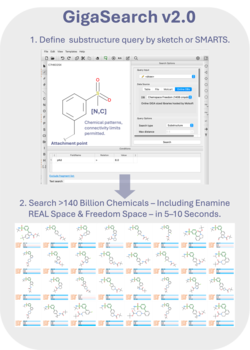
GigaSearch is MolSoft’s ultra-large chemical search engine designed to enable interactive substructure and pattern searches across chemical spaces containing billions to hundreds of billions of compounds. It allows users to explore vendor and virtual libraries at a scale that is impractical with conventional database indexing approaches, while maintaining fast response times suitable for iterative medicinal chemistry workflows.
The core technology behind GigaSearch is an optimized chemical fingerprint representation combined with statistically guided pruning of the search space. Instead of scanning entire databases, GigaSearch rapidly eliminates incompatible regions using fingerprint bit statistics, greatly reducing the number of structures that require exact substructure matching. Typical queries complete in seconds, even for giga-scale libraries.
GigaSearch supports flexible 0D and 2D chemical queries, including SMILES and SMARTS-based substructure definitions with detailed atom and bond constraints such as aromaticity, hybridization, charge, and ring membership. Search results can be interactively reviewed, filtered, and exported directly into ICM-Chemist or ICM-Pro for downstream analysis, docking, or lead optimization.
GigaSearch is available both as a hosted service accessed directly from ICM and as a locally installed solution for organizations that require on-premise deployment. This flexibility allows users to combine secure access to proprietary libraries with rapid exploration of massive commercial chemical spaces, making GigaSearch a practical entry point for giga-scale hit expansion and SAR exploration.
Read more about the method
here. |
Documentation |
New Neural Network–Based pKa Prediction
A new neural network model has been introduced for pKa prediction based on a chemical graph convolutional architecture with enhanced propagation through conjugated systems. The model captures long-range electronic effects, improving the treatment of resonance-stabilized functional groups and delocalized charge distributions. Training was performed using MolSoft’s in-house, diverse, manually curated pKa dataset.
MolSoft ICM has transitioned to updated ensemble neural network models for pKa prediction:
MODELS.MolpKaAcid = "pKaEnsAcid";
MODELS.MolpKaBase = "pKaEnsBase".
These ensemble models provide improved robustness and accuracy across chemically diverse compounds.
The updated pKa neural network significantly improves tautomer ranking by incorporating training data that include pKa differences (ΔpKa) between competing tautomeric forms. This results in more reliable identification of dominant tautomers under physiological and user-defined conditions.
A new GPU-accelerated formal charge assignment workflow has also been implemented using the neural network pKa models combined with a protonation-state system equilibrium calculation. This enables fast and physically consistent determination of protonation states and formal charges for large compound sets, supporting high-throughput ligand preparation, docking, and virtual screening.
| Documentation |
Other Improvements
Binary MPO Classification
Binary classification using Multi-Parameter Optimization (MPO) and Random Forest is a method for categorizing compounds into one of two groups (e.g., active/inactive, toxic/non-toxic, or drug-like/non-drug-like) based on multiple molecular properties. Instead of ranking compounds on a continuous scale, this approach applies a pass/fail decision based on predefined criteria.
|
Documentation|
New Training/Test Split Tools
Training/Test Split Tools: You can now split your data using either a simple random percentage-based method or the Kennard–Stone approach. Kennard–Stone offers maximum dissimilarity or hierarchical clustering options to ensure a more representative and diverse training set.
|
Documentation|
Version 3.9-4
Introducing Molsoft ICM-Pro Version 3.9-4 and New Product Releases
We're excited to announce the latest updates to MolSoft's ICM-Pro software. Below is a summary of the new products, features, and enhancements. For a complete list, please refer to the Release Notes and visit the What's New page on our website. You can download the latest version from our Support Site now.
The ICM-Pro + VLS software has undergone significant updates and improvements in its built-in functionalities for modeling, docking, GUI, and visualization. These enhancements include pre-built models in MolScreen for quickly predicting the target properties and activities of compounds. Notable new features encompass advanced MD functionalities, new AI models and AI layers for property and target prediction, extended cheminformatics functions, an improved 3D ligand editor, and direct access to AlphaFold models, as reviewed below.
Additionally, new modules have been developed for specialized GPU hardware. These modules are licensed separately from ICM-Pro and can be operated independently or launched via ICM-Pro + VLS.
This version of ICM has already demonstrated significant potential in pre-clinical lead discovery for
challenging targets such as BCL2, Menin , FLT3/IRAK4 and PPTP2N.
New GPU Empowered ICM-Pro Modules for Screening Ultra-Large Chemical Catalogs
GINGER - Fast and Accurate Neural Network Conformer Library Generation
Introducing GINGER (Graph Internal-coordinate Neural-network conformer Generator with Energy Refinement), our groundbreaking tool for high-quality conformer library generation on GPUs. GINGER is designed for lightning-fast performance, making it ideal for various molecular modeling and computer-assisted drug discovery workflows such as 3D ligand-based virtual screening using RIDE or fast GPU docking RIDGE. Learn more about GINGER on our website and read the newly released publiation describing the method or try an online demo of GINGER here.
GINGER is a standalone module which requires a separate license key it is also compatible with ICM-Pro and can be licensed for work stations or clouds designed for high-performance batch job management. Library conversion via GINGER can also be undertaken as a Service by MolSoft.
RIDGE - Rapid Docking GPU Engine
RIDGE is MolSoft's high-speed, accurate structure-based virtual ligand screening method. With a docking speed of approximately 100 compounds per second using an NVIDIA RTX 4090 GPU, RIDGE is 1000 times faster than a single CPU core. This enables the screening of 10 million compounds in less than 30 hours on an affordable "gaming" GPU desktop, rivaling a 1000-core CPU cluster. RIDGE supports multiple GPUs, further boosting its computational efficiency. Note that RIDGE is an add-on to ICM-Pro and requires a separate license key. Discover more about RIDGE here.
GigaScreen - Deep Learning Approach for Screening Ultra Large Databases
GigaScreen leverages machine learning and deep learning to efficiently screen extremely large chemical databases. This protocol allows giga-sized libraries to be screened on a single machine, eliminating the need for costly computational resources or additional software. GigaScreen is included with the purchase of a RIDGE license. Find out more about GigaScreen here. GigaScreen searches can also be undertaken as a Service by Molsoft.
New ICM-Pro Developments in 3.9-4.
New Molecular Dynamics Features
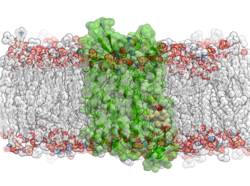
Molecular Dynamics (MD) in ICM uses the functions in OpenMM - new features in this release include: multiple GPU support, membrane embedding and MD simulations of complexes in VLS hitlists.
- Multiple GPU Support: Speed up your MD simulations by utilizing multiple GPUs
- Membrane Simulations and Embedding: The 'membrane' option activates specialized non-isotropic barostat in OpenMM (separate pressure along Z axis and tension in XY plane).
- MD simulations of complexes in VLS hitlists: MD can be run on a series of putative complexes in a VLS hitlist. The statistics on RMSD and RTCNN score drift is tabulated and the procedure is useful as an extra validation step in hit selection for experimental follow-up
|
Documentation |
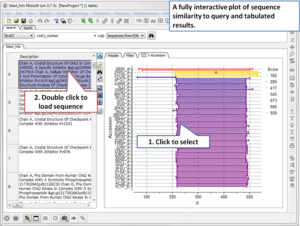
PDB Similarity Search
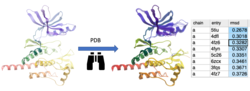
Search the PDB for similar structure/folds to the query protein. You can search by the whole protein, a selection or non-contiguous selection (e.g. ligand binding pocket). Documentation
Multiple Conformation and MD Snapshot Calculation Tools
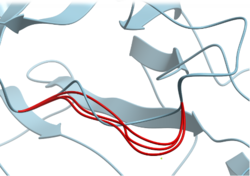
New tools facilitate the analysis of conformations from modeling or MD, including measurements of distance, RMSD, RMSF, Ligand Contacts, Torsion Changes, Area, Docking Score (RTCNN), and Cluster. Detailed Documentation is available here.
New AI Models in MolScreen
MolScreen is a set of high quality 2D and 3D AI/ML models for a broad range of pharmacology and toxicology targets. The models can be used for lead discovery or counter screening. A select number of models are provided with ICM-Pro but the full MolScreen panel requires a separate license key and is compatible with ICM-Pro. Some new models are provided in the latest release.
New Neural Network Classification Models are available for the following protein families.
- Kinase Family - 234 targets and built with 112564 ligands with AUC 99.81
- GPCR Family - 166 targets and built with 143566 ligands with AUC 99.65
- Peptidase Family -84 targets and built with 49290 ligands with AUC 99.87
- Ion Channel Family - 31 targets and built with 19732 ligands with AUC 97.93
- Phosphatase Family - 12 targets and built with 2661 ligands with AUC 99.33
- Cytochrome P450 - 14 targets and built with 34686 ligands with AUC 95.61
New Toxicity Models are also now available in MolScreen using neural network classification and regression models. These include:
- mcpCARCINOGEN - A carcinogen classification model.
- mcpFAMILY - A protein family ligand classification model.
- mcpPLASMA - Plasma protein binding prediction - Log10 of bound/free.
- mcphERG - hERG inhibitor and binder classification model.
Version 3.9-3
New Giga Search Libraries Available
Enamine Real (5.2 Billion Chemicals) and ZINC20 are now available in MolCart Giga Search or in ICM via the Chemical Search Window.
Torsion Profile Neural Network Prediction Engine
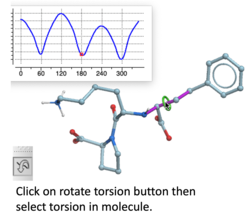
This tool is available with the rotate torsion tool in the GUI and the ICM 3D ligand editor. There is a free online demo version here and you can read more here. A paper will be published soon in JCIM describing this method.
Protonation States of Ligands vs pH
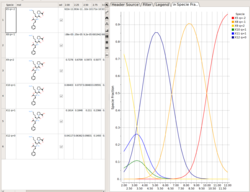 You can perform the following analysis of Protonation states vs pH using MolSoft's pKa Model:
You can perform the following analysis of Protonation states vs pH using MolSoft's pKa Model:
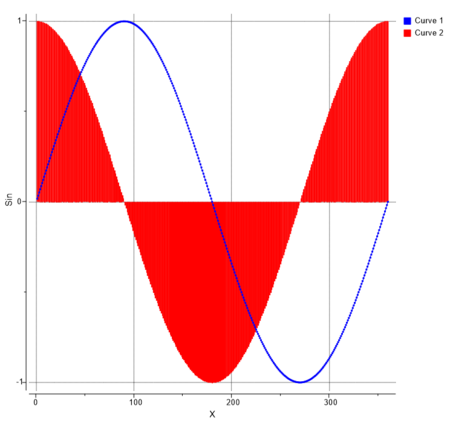
- Plot Concentration vs pH
- Plot Charge vs pH
- List Species at pH
Read more
here.
New Compressed Screening Databases - Dramatic reduction in size and increase in efficiency
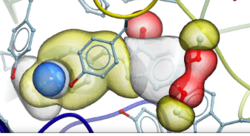
- New GIGA sized libraries for screening with RIDE are available including: NIH-SAVI, Enamine REAL, WUXI Galaxi. Download links to the new RIDE formatted databases are here.
- RIDE now supports screening of multiple databases in one run from the GUI or Command line.
- Introduced compressed new RIDE database format which uses ~4-6 times less disk space and faster reading.
Automated PROTAC Modeling
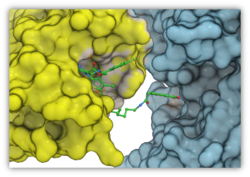
PROTACs are attracting substantial interest for modulating drug targets. In the latest version of ICM you can automatically model the interaction between the target protein and E3 ubiquitin ligase with the PROTAC molecule. The modeling is available in the GUI or via the protacModel.icm script. More...
New Peptide Docking Interface
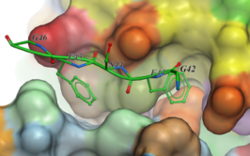
A new GUI interface for peptide docking and screening has been developed. Other new features include:
- extended .se polypeptide sequence format with unnatural amino acid modifications e.g. trp{hz3_F} is 5-fluoro tryptophane. Format also supports modeling of residue-residue cross-link 'staples'.
- secondary structure bias or restraints, for example one can keep a peptide alpha-helical during docking.
More...
GPU-Accelerated Molecular Dynamics (MD)

MD with GPU acceleration is incorporated in version 3.9-3 (Win, Linux only) it uses the functions in OpenMM - if you use this feature please cite OpenMM. More...
Search the PDB by Protein Structure Similarity
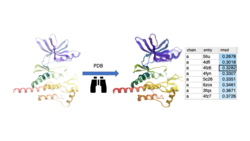
Search a query protein structure, pocket, or fold and compare for similarity to other structures in the PDB. A fully interactive hitlist of similar proteins is reported. More....
Historeceptomics

The historeceptomics (HR) platform is developed by GeneCentrix and reports tissue specific profiling for a drug molecule. It is a unique bioinformatics platform designed to identify mechanism of activity and predict unforeseen effects a chemical might have in the target tissue and off-target tissues. The new ICM version has an interactive interface and analysis tools to the HR platform.
More....
New Neural Net Virtual Screening Score for Better Compound Ranking in Docking Screens and 3D Ligand Optimization
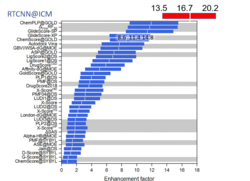
The RTCNN Score is a new Neural Network Score developed by MolSoft for structure-based docking and screening. RTCNN is a Convolutional Neural Net including layers that do Topological (chemical graph) convolutions and 3D Radial convolutions. More...
Atomic Property Fields - Ligand Based Screening
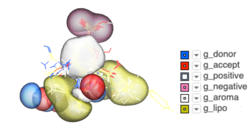
Some new options have been added to _chemSuper including -shape for shape matching only and the option to match Rigid has been added to the GUI .
Pi-Pi Interaction Visualization
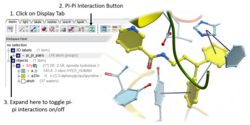
New Pi-Pi Interaction visualization tools. More...
Version 3.9-2
RIDE - Rapid Isoster Discovery Engine (RIDE) - Screen 500K Chemicals/Sec/GPU.
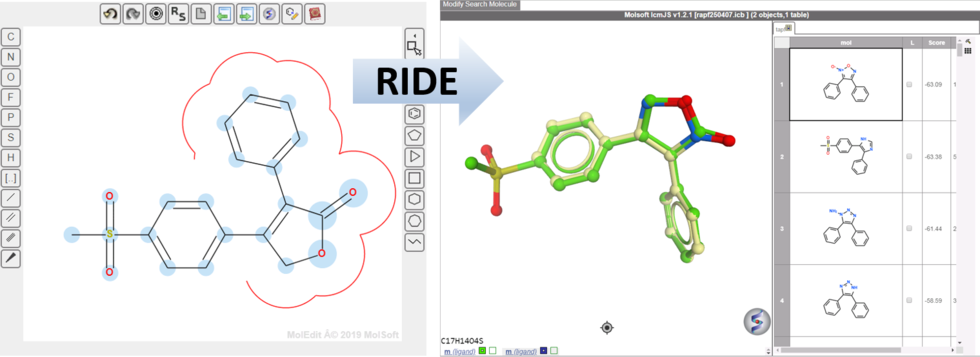
RIDE is a fast 3D molecular similarity search method based on Atomic Property Fields, developed at MolSoft. RIDE searches databases of compound conformers for molecules that are isosteric to the query, i.e. have similar 3D configurations and distributions of atomic properties.
GPU-based implementation is capable of searching ~0.5mln conformers/second on a single GPU card and perform 3D virtual screens of millions of compounds with the level of interactivity comparable to 2D searches. VLS benchmarking on DUDe indicates that RIDE searches produce enrichments on par with much slower standard flexible APF VLS.
RIDE applications include:
- Virtual screening - efficiently screen "giga-sized" libraries.
- Scaffold hopping - discover structurally novel chemicals based on a lead.
- Hit follow-up - quickly discover new chemicals with similar 3D pharmacophoric binding properties to your lead.
A simple web-based interface is provided for the ease of use by chemists, while batch script may be used by chemoinformatitians. In either format, RIDE allows fine-tuning of the queries to generate most desirable hit lists. This includes:
- Atom Weighting - Contributions of different portions of the molecule can be modulated with per-atom weights to reflect relative importance of certain moieties.
- Excluded Volumes meet Shape Matching - An envelope penalty can be applied to the regions that surround all or part of the query molecule to prioritize hits without bulky extensions in constrained regions.
RIDE Documentation
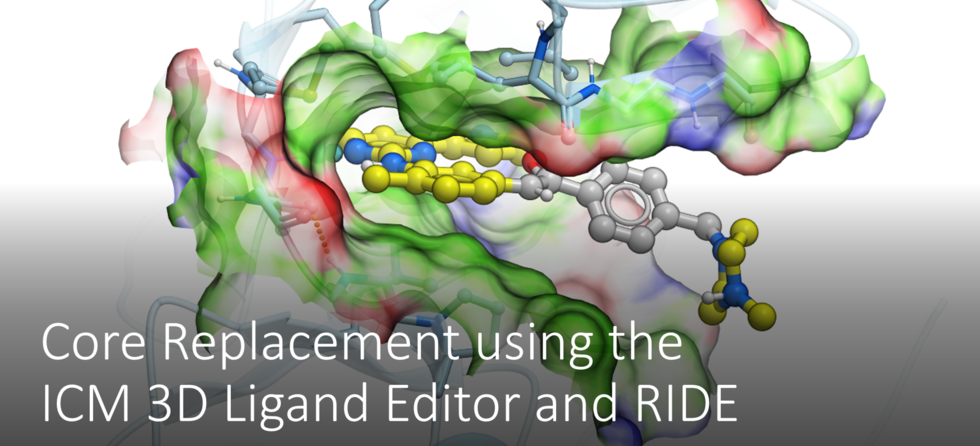
RIDE has also been incorporated into the 3D ligand editor for core replacement. Documentation
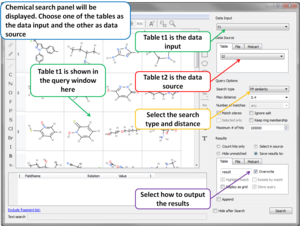
Giga-Search Enamine REAL database 1.2 Billion Chemicals in ICM
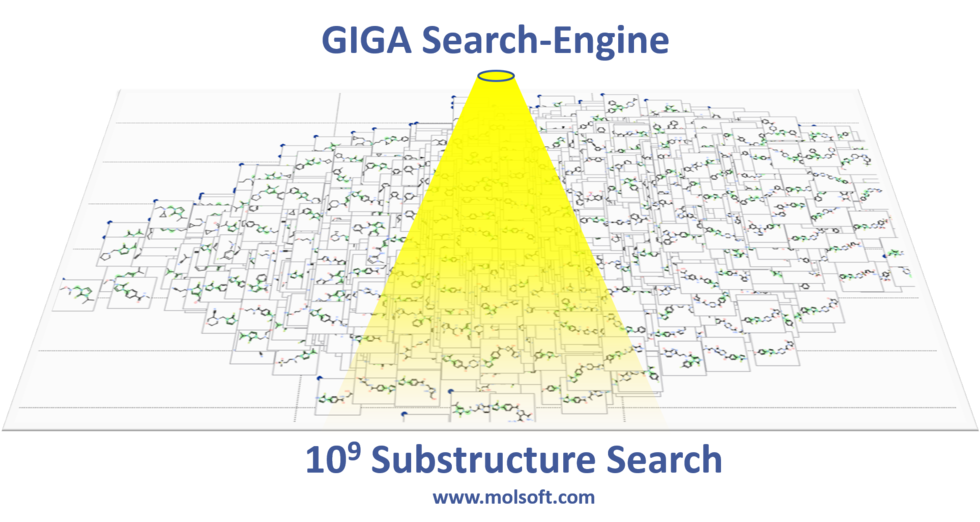
This is the first of its kind method to efficiently perform substructure search on very large chemical databases of >10^9 chemicals. You can read more about the method here.
You can perform a substructure search of Enamine's REAL database of >1.2 Billion chemicals inside the chemical search window in the ICM GUI.
[Documentation]
Blood Brain Barrier Score
The Blood Brain Barrier prediction score has been developed based on the method described By Gupta et al in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2019 - see DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01220
Blood Brain Barrier Score Documentation
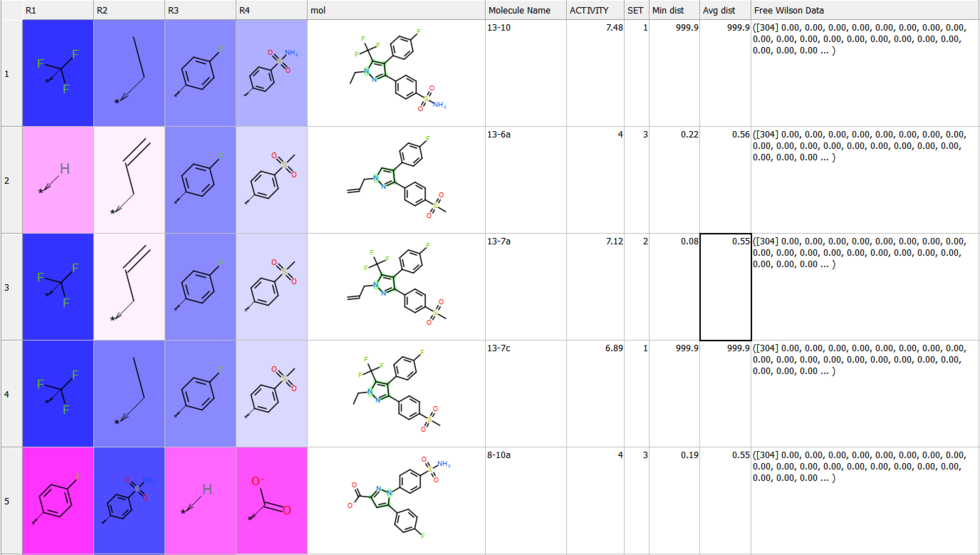
Free Wilson Regression Analysis
A new SAR analysis option has been included into ICM. The free wilson regression analysis can identify interesting combination of substituents which might have been missed by other SAR analysis methods.
[
Documentation]
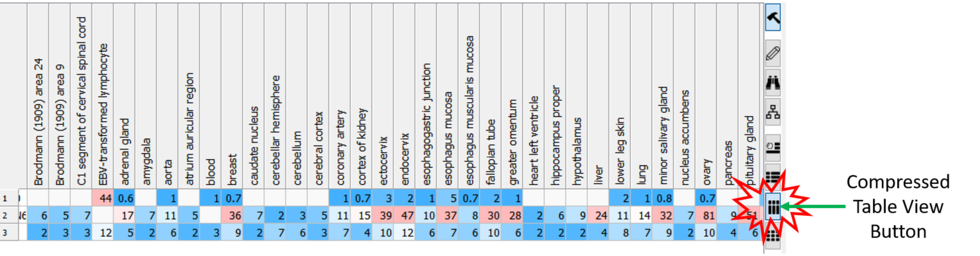
Compressed Table View
Sometimes if you have a very large table with many columns it is helpful to make the table more compact. [
Documentation]
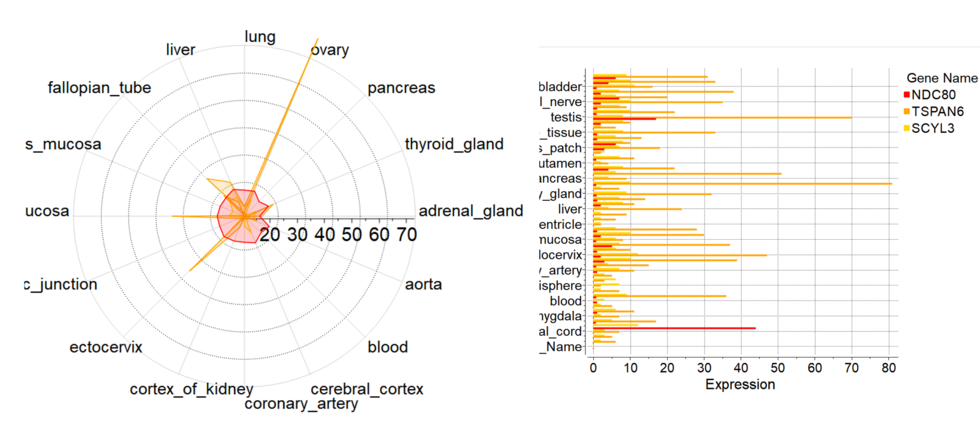
New Column Plot Tools
New column plot tools have been included into the latest version of ICM. To create new plot from GUI you need to select multiple numerical columns, click on plot icon and choose 'Plot columns' tab
There you can select more options:
- Log Scale
- Show statistics
- Label column for axis
- Plotting style including radar plots.
[
Documentation]
Version 3.8-7
Giga Search
This is the first of its kind method to efficiently perform substructure search on very large chemical databases of >10^9 chemicals. You can read more about the method
here.
You can perform a substructure search of Enamine's REAL database of >600 Million chemicals inside the chemical search window in the ICM GUI.
[
Documentation]
Structure- and Ligand- Based Screening
An easier way to break your screening jobs into chunks (parallel jobs) has been implemented. The variable:
proc = Number of processors
is now available in _chemSuper (APF ligand-based screening) and _dockScan (structure-based screening). In the graphical user interface you will now see the otpion to add "Number of Parallel Jobs" before you set the screening job running.

Protein Prediction
New predition of Cysteine residue reactivity method. [
Documentation]
De Novo Design
This method matches bonds in two ligands and then 'chimerizes' them along the bond. Input tables can be either docking hitlists or otherwise aligned 3D ligands, for example X-ray resolved ligands from the Pocketome entry. Same table can be used as both inputs to generate cross-hybrids within the same ligand set. Generally the idea is that one will review the list of potential chimeras and select some, or take all of them, and re-dock. After re-docking it is a good idea to compare to original ligands to see if chimeras work as intended and inherit positions of the parental moieties. [
Documentation]
Cheminformatics
- Tautomer search now available using the Chemical Search window. [Documentation]
- Topological descriptors now available using the Chemistry/Calculate Properties option. [Documentation]
- Predict Metabolic Oxidation [Documentation]
- New Chemical Visualization Method incoroporated into ICM - A Self Organized Map (SOM) is a way to represent higher dimensional data in 2D (or 3D) such that similar data is grouped together. Nodes in 2D map are called neurons. Each neuron is assigned a weight vector of the same dimensionality as input space. [Documentation]
- Multi Parameter Optimization Multi Parameter Optimzation (MPO) is a method that can be used to derive a score for the relative importance of a number of different chemical properties. You can create your own scores or use the ones built into ICM (e.g. CNS, Lipinski Rules or Quantitative Estimate of DrugLikeness (see https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22270643). MPO can be run on a 2D sketch 'mol' column or a SMILES column. [Documentation]
- Embedded Plots in Grid View If you have a column containing a plot you can now embed it in grid view. [Documentation]
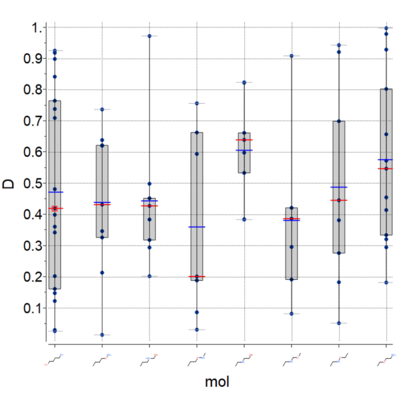
Plots
A new plot feature is to plot Median, Mean and IQR (see image) [
Documentation]
3D Ligand Editor
- Bioisostere Scan now available inside the 3D Ligand Editor.[Documentation]
Version 3.8-6
3D Ligand Editor
Plot R-Groups
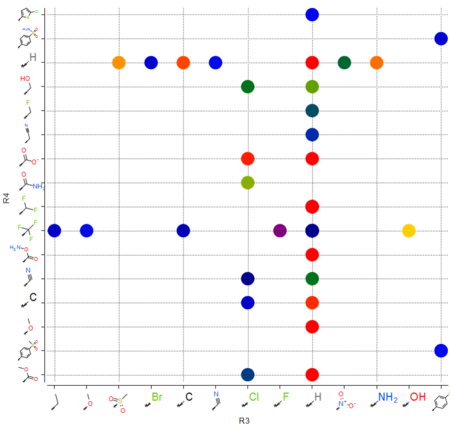 |
The option to plot chemical R-Groups in a scatter plot is now available. This is helpful with SAR analysis, for example you can plot R-groups generated from R-group library decomposition.[Documentation]
|
Find Bioisostere
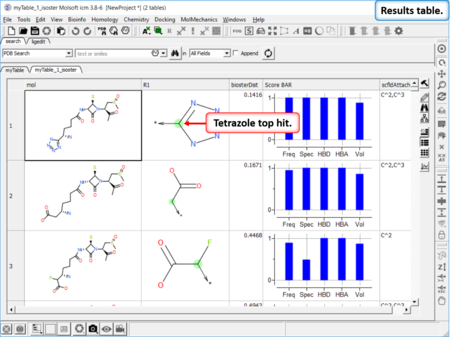 |
In drug design bioisosteres can be used to reduce toxicity, change bioavailability, alter metabolism and change activity of lead compound. Bioisosteres are chemical substituents with similar chemical or physical properties which produce broadly similar biological properties to another chemical compound. [Documentation] | [Webinar]
|
Matched Pair Analysis
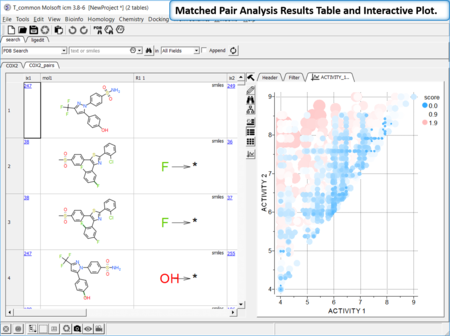 |
Matched Pair Analysis (MPA)can be used to study changes in chemical properties based on small well-defined structural modifications to the chemical structure. The method tries to find the Maximum Common Substructure and clusters by similarity. [Documentation]
|
Maximum Common Substructure Dendrogram
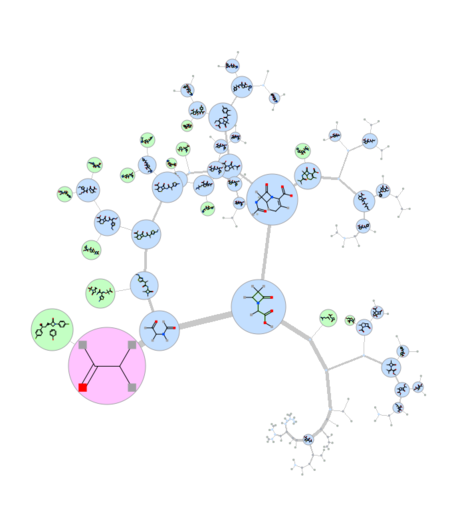 |
A fully ineractive dendrogram is a convenient way to visualize Maximum Common Substructure (MCS). The MCS method is K-greedy algorithm which simultaneously grows K different common substructures applying scoring and resorting on each step. [Documentation]
|
New Plot Options
Version 3.8-5
ICM Version 3.8-5 is now available in 64 bit for Mac, Windows and Linux. There is no RAM limitiation and so your experience with ICM's performance will be even better.
2D Ligand Complex Interaction Diagrams
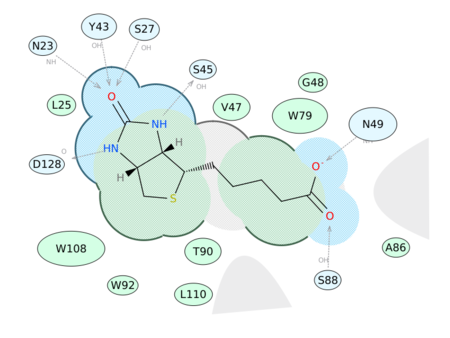 |
Generate a 2D Interaction Diagram of a ligand with the binding pocket. The image is annotated with hydrogen bonds and interacting residues. The residue interactions surface and proximity are represented by the size of the residue label and distance respectively. Grey parabolas and broken thick lines indicate solvent accessible regions and the ligand is shaded by property. [Documentation] | [Video]
A guide to the coloring and representation of the 2D display:
- Green shading represents hydrophobic region.
- Blue shading represents hydrogen bond acceptor.
- White dashed arrows represents hydrogen bonds.
- Grey parabolas represents accessible surface for large areas.
- Broken thick line around ligand shape indicates accessible surface.
- Size of residue ellipse represents the strength of the contact.
- 2D distance between residue label and ligand represents proximity.
- Covalently bound residue represented with thick black line around ellipse.
|
3D Ligand Editor
The ligand editor is a powerful tool for the interactive design of new lead compounds in 3D. It allows you to make modifications to the ligand and see the affect of the modification on the ligand binding energy and interaction with the receptor.
- Modification history table: Every ligand modification is stored and recorded in a chemical spreadsheet. Double click on the spreadsheet to view the change. [Documentation]
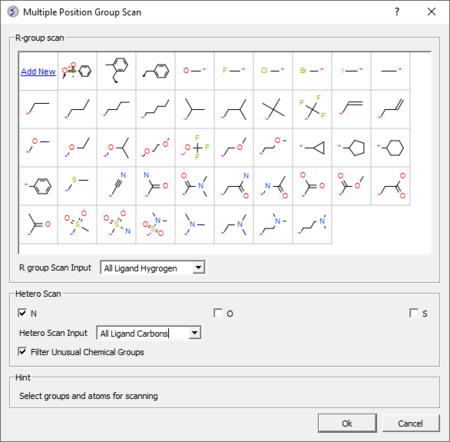
- Hetero atom scan around ligand: This option allows you to scan groups and hetero atoms at multiple locations on the ligand. [Documentation]
- R-group scan around ligand: This option allows you to scan groups and hetero atoms at multiple locations on the ligand. [Documentation]
- One click 2D interaction diagram: This option creates a 2D interaction map between the ligand and receptor. [Documentation]
- Simple way to analyze ligand-receptor contacts. [Documentation]
|
 |
IcmJS: Fast High Quality JavaScript 3D Molecule Viewer
Molecule Visualization and Graphics
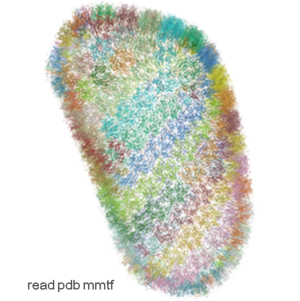
- Support for MMTF format. The Macromolecular Transmission Format (MMTF) is a new compact binary format to transmit and store biomolecular structural data quickly and accurately. MMTF is now supported in the latest ICM version it does not have any limitation on number of atoms and is easier to use than the original PDB. The image on the left shows the entire HIV-1 capsid (~2.4 million atoms PDB:3j3q).
- Retina support on Mac.
- Support for GROMACS trajectory files (Tools/Play Trajectory).
- Support for multi graphics windows. [Documentation]
- Quick ligand pocket interaction visualization. [Documentation]
- There is now an option for building a heatmap from data contained within a table. [Documentation]
- There is now an option to add annotations to a plot. [Documentation]
|
 |
Cheminformatics
 |
- Convert Prodrugs to Drugs and Drugs to Prodrugs using a set of reactions [Documentation]
- Flip boat to chair conformation in the Ligand Editor (Choose Advanced Button and select Apply Templates). Other templates will be added soon.
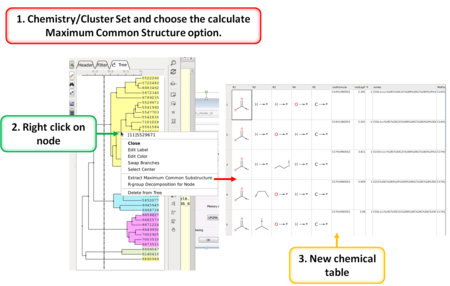
- Calculate Maximum Common Substructure [Documentation]
- R Group Decomposition from Clustering Node [Documentation]
- Improved pKa auto charge models. [Documentation]
- Auto close tree mode to make cluster trees more compact. [Documentation]
|
Docking and Screening
- Add docking restraints by selecting atoms in the receptor. An interacting moiety in the ligand can also be defined. [Documentation]
Protein Modeling and Design
Bioinformatics
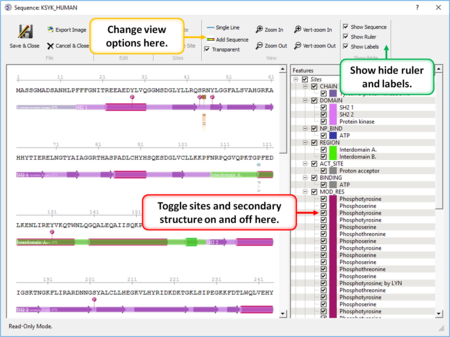 |
- Create a sequence alignment profile and plot it onto an alignment. [Documentation]
- Sequence Editor Display and edit sites on a sequence. [Documentation]
|
Version 3.8-4
MolScreen
- New Docking to Protein Pocket Classification/Regression models (dpc) [Documentation]
- Build a custom model panel [Documentation]
- Make a classification model based on your own data or directly from ChEMBL [Documentation]
- Make a APF Docking SAR model based on your own data or directly from ChEMBL [Documentation]
Docking and Screening
A method to calculate the ligand interaction fingerprint from a hitlist has been developed. The fingerprint is a bit string representing a contact with each atom. For specificity there is a special subset of bit strings which represent hydrogen bonding. [Documentation]
Cheminformatics
- Direct link to the ChEMBL databases allows you to search and output chemical and activity data to a chemical spreadsheet [Documentation].
- Direct link to the SureChEMBL chemical patent database [Documentation].
- Free radicals are now supported in 2D and 3D. [Documentation]
- Enumerate formal charge states. [Documentation]
3D Ligand Editor
- Explicit side-chain support has now been added. [Documentation]
- Minimize the ligand in full atom model inside the receptor as well as in the grid maps. [Documentation]
- An option to keep "tight waters" on receptor setup has been added. [Documentation]
- A more interactive way to impose tethers and distance restraints. Each restraint is placed in a table and the values of the restraint can be edited. [Documentation]
- A convenient way to close and clean up your ligand editor session. [Documentation]
Predicting the Effect of Mutation
Two new options:
- Predict the effect of mutation on Protein-Peptide. [Documentation]
- Predict the effect of mutation on Proein-Ligand. [Documentation]
Homology Modeling
New modeling options have been added and old ones improved. The modeling options are:
- Quick Model This option will provide a model by placement of the aligned polypeptide chain onto the template structure. The method is fast and is ideal if you want a quick model for visualization purposes. [Documentation]
- Full Model Builder This option will give you a fully refined model and can take many hours to complete the model building process. There are options to fully refine side-chains, refine side-chains and loops or undertake a full refinement. The refinement is undertaken using the ICM BPMC modeling method in the ICM force field which includes surface terms, electrostatics with the boundary element solution of the Poisson equation and side chain entropy terms. [Documentation]
- Multi-Template Model Editor. This option is ideal if you want more control over your model - particularly in loop regions or if you want to use multiple templates. It provides an interface to add new templates to a model and browse through multiple conformations of loop regions. It also provides an interactive visualization interface to see how well the residues in your model falls into the Ramachandran Plot and how good the omega angles are. [Documentation]
Learn and Predict
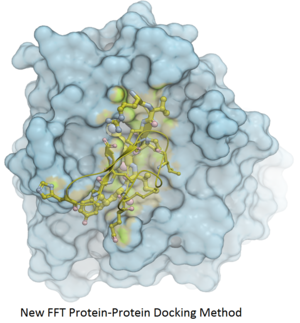
Protein-Protein Docking
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) docking method has been developed.
The docking method contains two stages:
- The first stage uses a simplified scoring function representing steric fit and hydrophobic/hydrophilic contact matching. FFT is then used for translational search using systematic search of rotations from 60x27 (coarse) to 256x125 (fine) orientations.
- The second stage rescores the top 3000-20000 solutions with a more accurate energy function including electrostatics and SAS-based solvation. The conformations are then clustered using contact fingerprints.
December 20th 2014: Version 3.8-3 Released
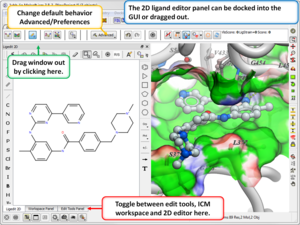
3D Ligand Editor
- The 2D editor can now be embedded in the ligedit tab panel (see image). Any changes in the 2D editor can be committed to 3D with a single click. Documentation
- Any change in 3D can be automatically saved to a spreadsheet but now if you click and hold on the button you can add a tag or comment to the saved chemical in the spreadsheet. Documentation
KNIME
- New MolCluster node is available - you can cluster either by fingerprints or by numerical column selection.
The output will contain two additional columns:
- 'cl' : cluster number
- 'dist_to_cent' : distance to cluster center. Documentation
Cheminformatics
- Improvements have been made to hierarchical grouping in tables. Documentation
Graphics
- Surface and pocket meshes are now grouped and linked directly to the ligand object.
September 1st 2014: Version 3.8-1 Released
New features include:
Modeling
- MERSi: Mutation Effects with Relaxation of Side-chains in Internal coordinates.
- Build homology models with rigorous refinement in batch (see Homology/Batch Build and Refine).
- Loop Grafting - transfer a loop region from one protein to another. Documentation
- Build peptides and make mutations using unusual amino acids. A table of 250 non-standard Amino Acids added and enabled for the mutation tool.
- Protein Sculpting can be used to model the interaction of two connected domains. You simply drag the molecules around a hinge region followed by a minimization. Documentation
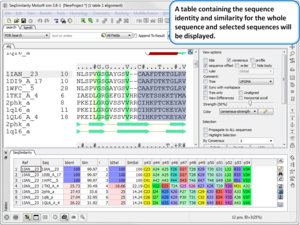
Sequence and Alignment
- Calculate Global or Local Sequence Similarity and Identity in an Alignment. Documentation
- Sequence drag'n'drop between sessions is now supported.
- Multi-line sequence alignment annotations are now supported.
Cheminformatics
- Extensive chemical dictionary is now available in the molecule editor.
- Direct search of the Crystallography Open Database (COD). The COD is an open-access collection of crystal structures of organic, inorganic, metal-organic compounds and minerals, excluding biopolymers.
- Direct interface in GUI for searching PubChem. Documentation
- Match chemical 2D sketch to PubChem and extract PubChem CID or ID number (Use Insert Column and choose Function Chemical PubChem).
- New set of pre-prepared common covalent binding mechanism reactions for covalent ligand docking. Documentation
February 5th 2014: MolSoft Releases New ICM Version 3.8
MolSoft is excited to release a new version of ICM. Please download the new version from www.molsoft.com/download.html. The Release Notes contain a complete list of new features and fixes but the key ones are listed below.
Graphics
- Anaglyph 3D can be viewed using low cost 3D glasses and without any expensive 3D compatible hardware or monitors. It can be viewed directly on your computer's monitor, conference room projector, or on your iPad or android device. You can also print the image out rendered for viewing in 3D. Any red and cyan glasses will work well. [More Information] and [Documentation]
- MolSkin MolSkin is a new macro that instantly makes publication quality graphics for surfaces and colors contact patches. [Documentation]
- Movies from Slides A simple way to make a movie is by making a set of slides containing the scenes and then let ICM package them into a movie file. [Documentation]
Docking and Screening
- SCARE The SCARE method allows you to take into account induced fit of the receptor upon ligand docking. The method systematically scans pairs of neighboring side-chains and replaces them with Alanine and docks a ligand to each of the "gapped" models. A full description of this method and validation is published here. [Documentation]
- MolScreen is a set of high quality 2D fingerprint and 3D pharmacophore models for a broad range of pharmacology and toxicology targets.
The models can be used for lead discovery or counter screening. The models use MolSoft's 2D QSAR/Fingerprint and 3D Atomic Property Fields ( Totrov 2008) methods. [More Information] and [Documentation]
- Fragment Screening Screen a database of chemical fragments which are then ranked by p-value providing a quantitative measures of confidence that a fragment is a true active and binds in the specific pose in absolute terms, instead of just ranking it versus other fragments. [Documentation]
- Docking directly from table The ability to dock directly from a loaded chemical table gives you some flexibility about which chemicals you wish to dock from a table and makes docking more interactive and more convenient. [Documentation]
New Data Search and Retrieval Options
- Blast Search Now you can BLAST search the NCBI database directly in the ICM GUI. [Documentation]
- Pocketome Search The Pocketome (www.pocketome.org) is an encyclopedia of conformational ensembles of all druggable binding sites that can be identified experimentally from co-crystal structures in the Protein Data Bank. [Documentation]
- Drugbank Search The DrugBank (http://www.drugbank.ca/)database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. [Documentation]
- UniProt Search The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt) is a comprehensive resource for protein sequence and annotation data. [Documentation]
Cheminformatics
- Fingerprints Extended Connectivity Fingerprints (ECFP) have been added.
- Chemical Search Chemical Search dialog allows to select an existing chemical table for Molcart or local search (see image).
- InChI is now supported.
- ToxScore A ToxScore function is now available in the Insert Column Dialog. [Documentation]
- Atomic Property Fields A chemical table can now be clustered by Atomic Property Fields (see Chemistry/APF Tools}
- Export to Excel The 2D chemical sketch is now exported to Excel. [Documentation]
January 24th 2014: Introducing MolScreen - A Panel of >360 High Quality Screening Models
 MolScreen is a set of high quality 2D fingerprint and 3D pharmacophore models for a broad range of pharmacology and toxicology targets. The models can be used for lead discovery or counter screening. The models use MolSoft's 2D QSAR/Fingerprint and 3D Atomic Property Fields ( Totrov 2008 ) methods.
MolScreen is a set of high quality 2D fingerprint and 3D pharmacophore models for a broad range of pharmacology and toxicology targets. The models can be used for lead discovery or counter screening. The models use MolSoft's 2D QSAR/Fingerprint and 3D Atomic Property Fields ( Totrov 2008 ) methods.
The models can be screened directly using MolSoft's ICM-Pro + VLS software. Alternatively we can screen a set of chemicals for you via our contract research services. Please contact us for more information about how to use MolScreen.
March 7th 2012: ICM Version 3.7 Released
MolSoft is excited to announce the release of ICM version 3.7-2c. The new version can be downloaded from our support site here.
The key new features are described below but for a detailed list please see the release notes.
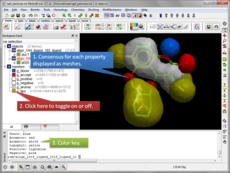 Atomic Property Fields APF is a 3D pharmacophoric potential implemented on a grid (Totrov 2008 and 2011 ). APF can be generated from one or multiple ligands and seven properties are assigned from empiric physico-chemical components (hydrogen bond donors, acceptors, Sp2 hybridization, lipophilicity, size, electropositive/negative and charge). An independent study found that APF is most accurate method for chemical superposition and ligand-based 3D virtual screening compared to several other commercial and academic softwares. (Giganti et al 2010).
Atomic Property Fields APF is a 3D pharmacophoric potential implemented on a grid (Totrov 2008 and 2011 ). APF can be generated from one or multiple ligands and seven properties are assigned from empiric physico-chemical components (hydrogen bond donors, acceptors, Sp2 hybridization, lipophilicity, size, electropositive/negative and charge). An independent study found that APF is most accurate method for chemical superposition and ligand-based 3D virtual screening compared to several other commercial and academic softwares. (Giganti et al 2010).
- Ligand based screening using APF [more..]
- Calculate pairwise APF scores [more..]
- Generate a consensus pharmacophore [more..]
- Superimpose ligand binding sites by Atomic Property Fields [more..]
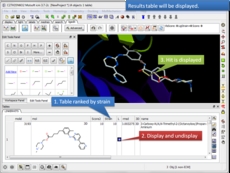 3D ligand Editor The ligand editor is a powerful tool for the interactive design of new lead compounds in 3D. It allows you to make modifications to the ligand and see the affect of the modification on the ligand binding energy and interaction with the receptor.
3D ligand Editor The ligand editor is a powerful tool for the interactive design of new lead compounds in 3D. It allows you to make modifications to the ligand and see the affect of the modification on the ligand binding energy and interaction with the receptor.
- Multiple Receptor Docking in the 3D ligand editor [more..]
- Chemical fragment linking in the 3D ligand editor [more..]
- Dock to APF fields in the 3D ligand editor [more..]
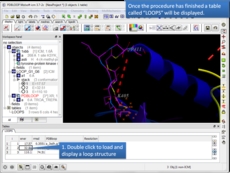
Protein Modeling Inside ICM there are many features for homology modeling and loop modeling. This new option can be used if you have a gap in your protein and you want to find loops in the PDB which fit the gap.
- New protein loop design method is now available. [more..]
Chemisty A couple of new options in the Chemistry menu.
- Calculate ligand strain [more..]
- Calculate ligand entropy [more..]
 "Pipe-able" Scripting in ICM New options to pipe icm commands and scripts.
"Pipe-able" Scripting in ICM New options to pipe icm commands and scripts.
- Easy way to write pipe-able scripts (see $ICMHOME/molpipe/*.icm).
- Easy way to add parallelism to unix/mac ICM scripts: fork with pipe option ($ICMHOME\molpipe\*.icm)
Other New Features and Options
- Desciption of all the fields in the docking .tab file [more..]
- Easy manipulation of internal coordinates copy/paste and drag'n'drop between icm sessions ( images, molecular objects, meshes, tables ) [more..]
|









 You can perform the following analysis of Protonation states vs pH using MolSoft's pKa Model:
You can perform the following analysis of Protonation states vs pH using MolSoft's pKa Model:








 [Documentation]
[Documentation]
 [Documentation] | [Example]
[Documentation] | [Example]










 MolScreen is a set of high quality 2D fingerprint and 3D pharmacophore models for a broad range of pharmacology and toxicology targets. The models can be used for lead discovery or counter screening. The models use MolSoft's 2D QSAR/Fingerprint and 3D Atomic Property Fields ( Totrov 2008 ) methods.
MolScreen is a set of high quality 2D fingerprint and 3D pharmacophore models for a broad range of pharmacology and toxicology targets. The models can be used for lead discovery or counter screening. The models use MolSoft's 2D QSAR/Fingerprint and 3D Atomic Property Fields ( Totrov 2008 ) methods.