| Prev | 2.7 Molecule intro | Next |
|
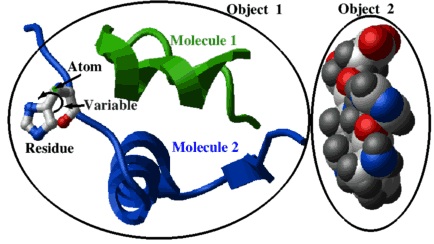
Molecules are the main inhabitants of the ICM shell. The shell can contain many objects, each of which can be a soup (this expression belongs to my friend Gert Vriend) of separate molecules. Molecules, in turn contain residues and atoms. ICM can handle both raw objects, as they come from a PDB file or a mol-file, and a fully prepared for molecular modeling "ICM"-objects. |
 |
The non-ICM objects can be visualized, but they need to be converted into ICM-objects to perform the most interesting modeling operations. To specify the subsets of objects, molecules, residues, atoms and internal variables, you need to learn the language of molecular selections.
A quick preview of the selection language, using the picture above as an example:
display a_2. cpk # object selection (the second object) display a_1.1 ribbon green # molecule 1 from object 1 display a_1.2/his xstick # residue his12 shown as balls and sticks color a_/1.2/12/n* xstick blue # atoms: color nitrogens in blue
For an in-depth description of selections, read the next section.
| Prev subset | Home Up | Next selection |