| Prev | ICM User's Guide 16.13 Generate Stereoismers | Next |
Theory
Isomers are molecules which have the same chemical formula and sometimes the same kind of bonds but in which the atoms are arranged differently.
Structural isomers have different atom-to-atom connections e.g. propanol (C3H8O or C3H7OH) has two isomers Propan-1-ol and Propan-2-ol.
Diastereomers are not mirror images and have different internal dimensions (e.g. dihedral angles and distances between non-bonded atoms). They can be configurational diastereomers (which can be interconverted only by breaking bonds or by changing the configurations of stereocenters) or conformational diastereomers (which can be interconverted by rotation about bonds - including chair flips or by lone pair inversion .
Enantiomers have identical internal dimensions, and are nonsuperimposable mirror images. Enantiomers can be configurational and conformational.
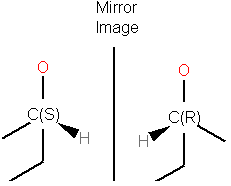
Enatiomers are distinguished based on the Latin terms for left (sinister) and right (rectus). In some cases where the handedness is unknown a chiral center can be labeled "RS"or unknown.
To enumerate and display in a separate table the stereoisomers of selected compounds.
- Select the compound(s) in the molecular table. Selected compounds are highlighted in blue.
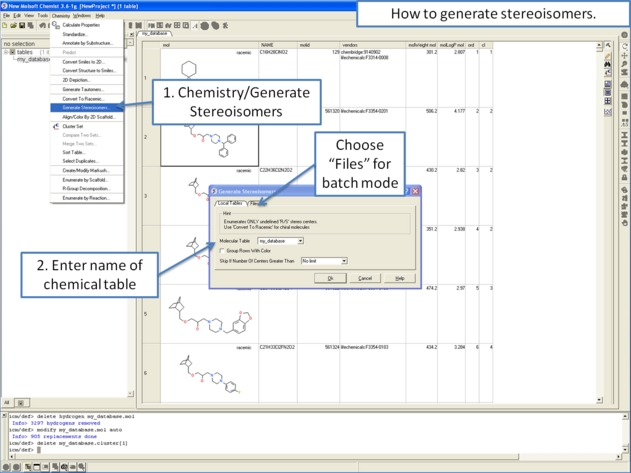
- Right click in the table and select the option Chemistry/ Enumerate stereoisomers. Or select the Chemistry menu and choose Generate Stereoisomers. If you generate stereoisomers via the Chemistry menu you will get a dialog box whereby you can run the process in batch mode. There is also an option to color stereoisomers from the same compound with the same color.
- The compounds will be displayed in a separate molecular table called STEREOISOMERS.
From the Chemistry Menu:
From a chemical spreadsheet:}
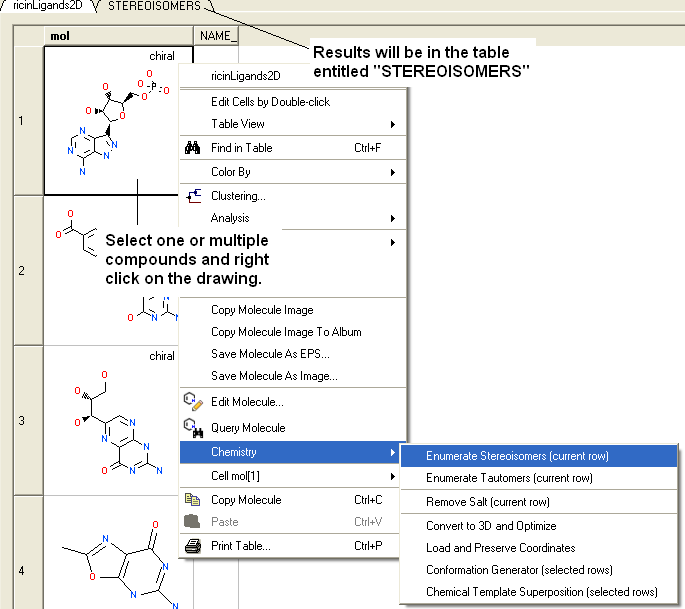
| NOTE: Only centers with unknown chirality will be enumerated. |
| Prev Convert to Racemic | Home Up | Next Align/Color by 2D Scaffold |