| Prev | ICM User's Guide 22.4 Working with PDB Structures | Next |
[ PDB Search | Convert ]
OverviewThis lesson will take you through the basics of reading and displaying PDB structures and their conversion into ICM objects. Topics covered include:
22.4.1 PDB Searching |
Objective
To display the crystal structure of a G-Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR).
Background
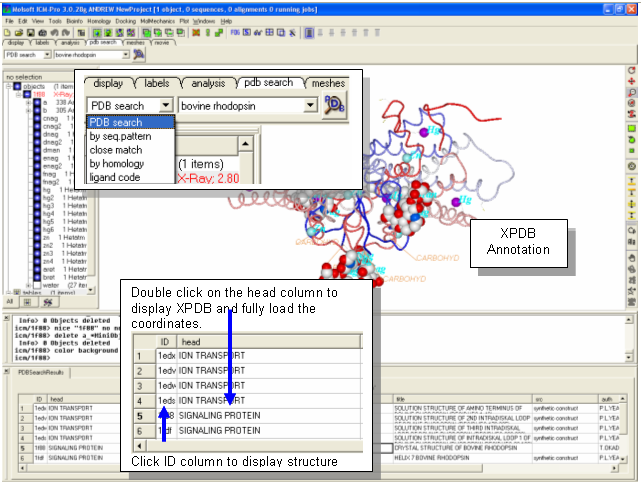
Using ICM it is easy to quickly search and download PDB files using the .pdb search. tab.
Instructions
- Click on the PDB Search Tab
- Type bovine rhodopsin into the search box and click the button next to it. A table of hits will be displayed at the bottom of the GUI.
- Double click on the ID field of structure 1F88 to display the structure.
Notes and things to try:
- Try searching for a PDB file by sequence or homology. Use the drop down menu next to the PDB search box to define which kind of search you are undertaking.
Manual References (Web Links)
22.4.2 Converting a PDB File into an ICM Object |
Objective
To convert a PDB file into an ICM object.
Background
Sometimes it is necessary to have a PDB file in the form of an ICM molecular object. For example, it's a convenient way to list and/or to change a torsion angle (or a series of them). It is also necessary to convert PDB files into ICM objects for ICM functions such as docking. There are two principally different modes of conversion. In the default mode the program looks at the residue name and tries to find a full-atom description of this residue in the icm.res file. This search is suppressed with the exact option. Hydrogen atoms will be added if the converted residues are known to the program and described in the icm.res library.
Instructions
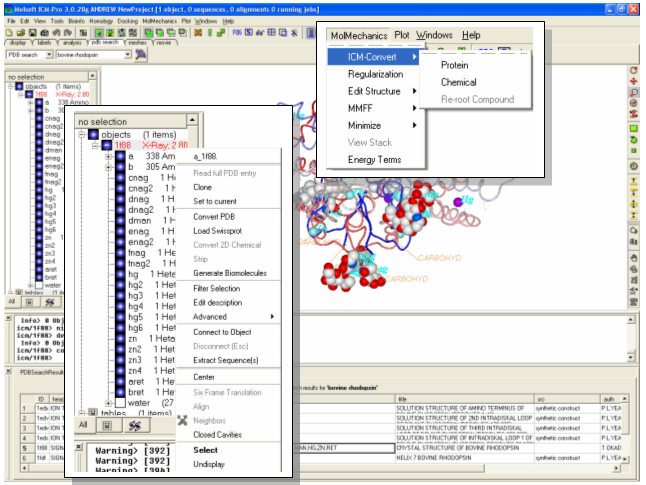
To convert a PDB file into an ICM object (**IMPORTANT Do not use this method for small molecules (sdf, mol, mol2) use MolMechanics/ICM-Convert/Chemical) :
- Right click on the PDB file name in the ICM Workspace and select Convert PDB OR select MolMechanics/ICM-Convert/Protein
Notes and things to try:
- Within the right click menu there are many other useful options such as: clone- which copies the current object; set to current - if multiple structures are loaded you can set this object to be the current one; Extract Sequence(s) . extracts the sequence of the whole object or the subunit depending where you click. Experiment with some of these options.
- The ICM workspace will tell you whether a structure is an X-Ray or an ICM object.
| Prev 3D Documents | Home Up | Next Sequence and Alignment Tutorial |